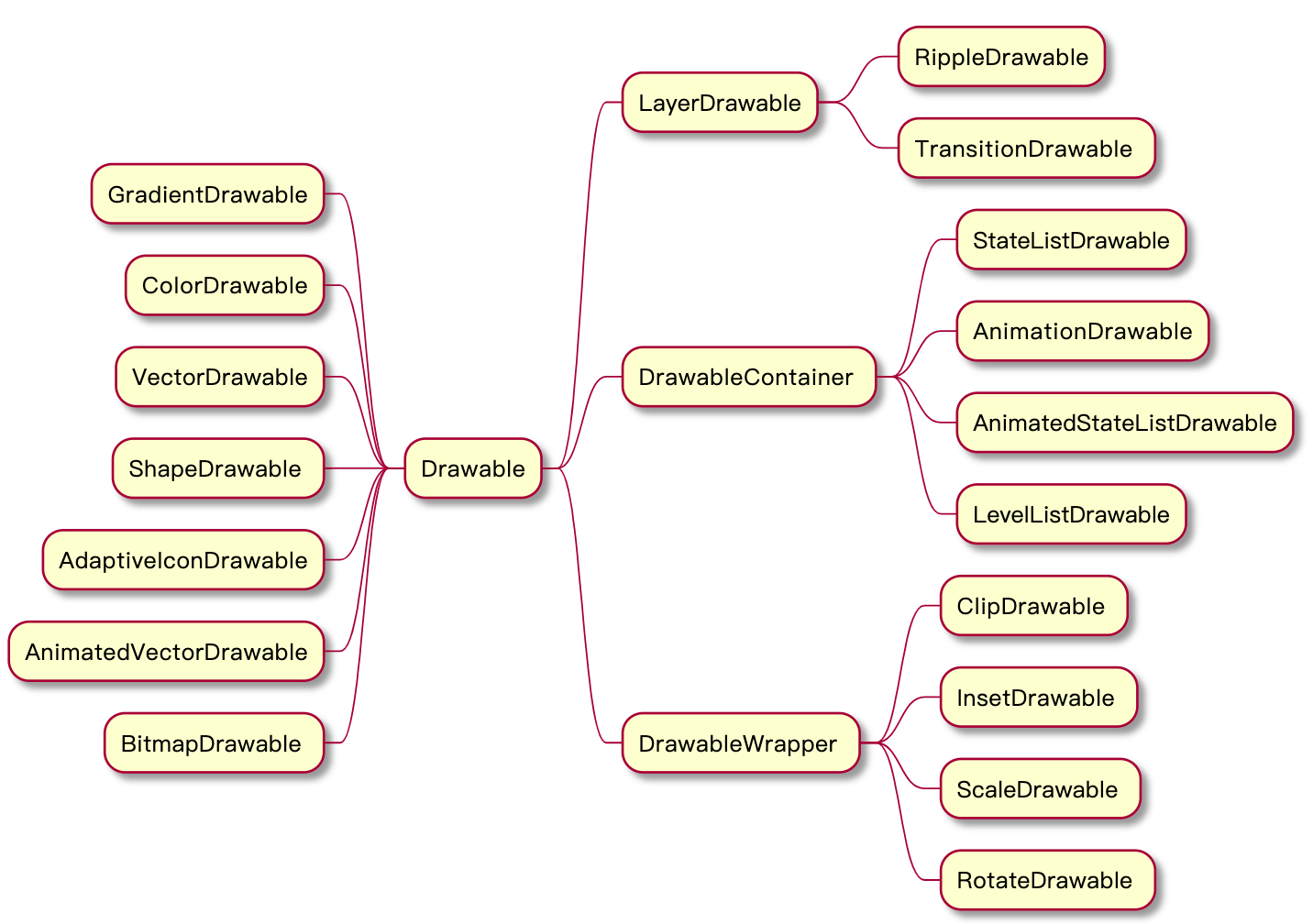
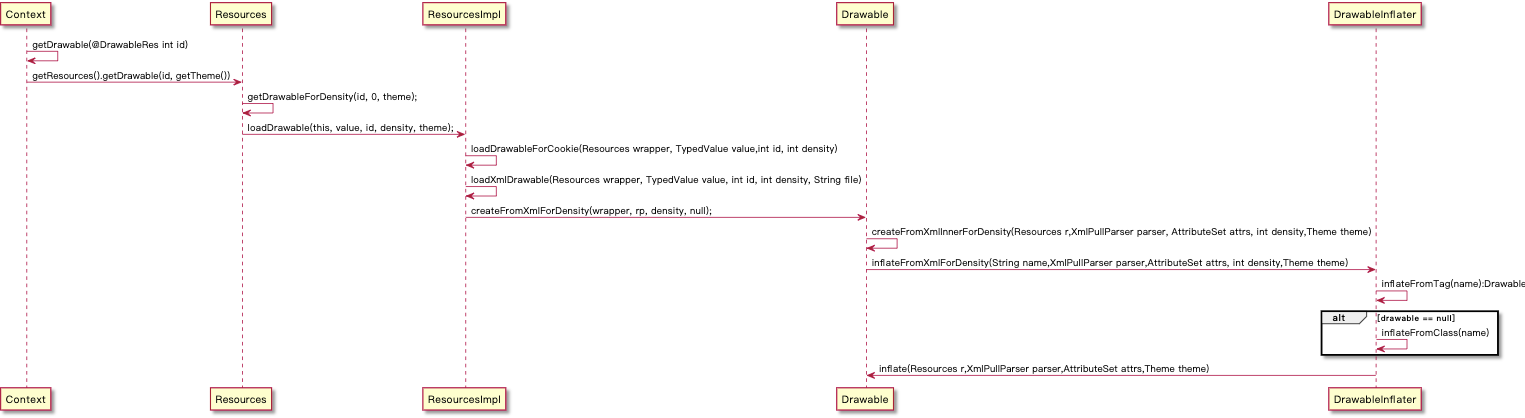
Drawable表示一种可以在Canvas上进行绘制的抽象的概念,它有很多种,常见的如颜色和图片都可以是一个Drawable。
1、首先,它的使用比较简单,在xml里已经定义了大量的属性方法,我们只要熟悉各个属性的ui效果和特点就可以自己组合各种的界面效果。 2、其次,它的实现成本比自定义View低,一些比较简单的、定制性、重复性的UI效果使用drawable将会缩小开发成本。但是一些比较复杂的ui场景,drawable却表现不出自定义view的那种效果。 3、相比较于图片而言,drawable占用空间更小,这样有利于缩小apk的体积。
Drawable尽管对于应用程序通常不可见,但Drawable可以采用多种形式:
Bitmap:最简单的Drawable,一个PNG或JPEG图像。
Nine Patch:是对PNG格式的扩展允许它指定如何对其进行拉伸和放置的信息
Vector:向量:在XML文件中定义的可绘制的一组点,线和曲线以及相关的颜色信息。 这种类型的绘图可以缩放而不会损失显示质量。
Shape:形状:包含简单的绘图命令而不是原始位图,允许在某些情况下调整更好。
Layers:图层:一个可绘制的复合物,它在彼此顶部绘制多个底层可绘图。
States:状态,一个复合drawable,根据其状态选择一组drawable中的一个。
Levels:级别:一个复合drawable,根据其级别从一组drawable中选择一个。
Scale:比例尺:一个可绘制的单个子组合可绘制的组合,其整体大小根据当前级别进行修改。
最终的inflateFromTag方法
@NonNull
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private Drawable inflateFromTag(@NonNull String name) {
switch (name) {
case "selector":
return new StateListDrawable();
case "animated-selector":
return new AnimatedStateListDrawable();
case "level-list":
return new LevelListDrawable();
case "layer-list":
return new LayerDrawable();
case "transition":
return new TransitionDrawable();
case "ripple":
return new RippleDrawable();
case "adaptive-icon":
return new AdaptiveIconDrawable();
case "color":
return new ColorDrawable();
case "shape":
return new GradientDrawable();
case "vector":
return new VectorDrawable();
case "animated-vector":
return new AnimatedVectorDrawable();
case "scale":
return new ScaleDrawable();
case "clip":
return new ClipDrawable();
case "rotate":
return new RotateDrawable();
case "animated-rotate":
return new AnimatedRotateDrawable();
case "animation-list":
return new AnimationDrawable();
case "inset":
return new InsetDrawable();
case "bitmap":
return new BitmapDrawable();
case "nine-patch":
return new NinePatchDrawable();
case "animated-image":
return new AnimatedImageDrawable();
default:
return null;
}
}
| shape | count | ratio |
|---|---|---|
| shape | 833 | 73% |
| selector | 240 | 21% |
| layer-list | 50 | |
| animated-rotate | 7 | |
| animation-list | 5 | |
| vector | 3 | |
| rotate | 2 | |
| level-list | 1 |
我的项目里面,统计了drawable文件的总数是1140, 其中最多的是shape,总数833,占比73%, 其次是selector,总数240,占比21%, 这两个加起来占比达到94%. 而这两种类型都是差别很小的,主要是背景颜色和圆角角度不同,导致了大量的文件的产生, 而且对于这类的文件命名也是很难统一,从而难以达到复用的效果,有时候找一个目标文件, 远远没有自己创建一个新的Drawable文件快,所以渐渐的会导致此类文件的爆炸式增长。 从而增大apk的体积。
通过xml解析流程,我们可以发现其中的奥妙,xml也只是根据具体的标签直接new出来对应的是类,然后再直接设置具体的参数, 如此一来,我们完全可以做到,自己创建具体的对象,然后设置参数,这样就避免了xml解析这一步,
mViewBinding.lineDrawable.background = shapeDrawable(this) {
lineShape()
dash(10, 5)
strokeColor(Color.RED)
strokeWidth(2)
}
mViewBinding.stateListDrawable.background = selectorDrawable {
pressedDrawable {
shapeDrawable(this@MainActivity) {
solidColor(Color.BLUE)
radius(8)
}
}
defaultDrawable {
shapeDrawable(this@MainActivity) {
solidColor(Color.GRAY)
radius(8)
}
}
}
具体的项目可以在封装一次,减少每次的创建条件设置,这样只需要传递具体的参数就可以,便于复用, 当然,项目也封装了几个通用的方法。比如:
fun shapeDrawableColorInt(context: Context, @ColorInt colorInt: Int = Color.WHITE, radius: Int = 0) =
shapeDrawable(context) {
solidColor(colorInt)
radius(radius)
}
fun shapeDrawableColorRes(context: Context, @ColorRes colorRes: Int, radius: Int = 0) =
shapeDrawable(context) {
solidColorRes(colorRes)
radius(radius)
}
比起xml方式可以提升性能:避免xml解析流程 复用这些代码:比xml管理方便
implementation 'io.github.weiggle:drawable:1.0.1'