myoSarcHandObjHoldRandom-v0-model.mp4
Solved task - myoSarcHandObjHoldRandom-v0
The dexterous human hand requires the coordination of multiple highly redundant muscles, which have complementary and antagonistic effects on various joints. This musculoskeletal model is comprised of 29 bones, 23 joints, and 39 muscle-tendon units. Our objective is to simulate the coordination of these bones and muscles for different tasks via reinforcement learning.
In this repository, we try to solve musculoskeletal tasks with Double DQN reinforcement learning. A transformer model has been used as the base model architecture.
The goal of challenge is to push our understanding of physiological motor-control responsible for nimble and agile movements of the human body. we are focusing on developing controllers for contact rich dexterous manipulation behaviors.
-
MyoSuiteis a collection of musculoskeletal environments and tasks simulated with the MuJoCo physics engine and wrapped in the OpenAIgymAPI to enable the application of Machine Learning to bio-mechanic control problems. -
PyTorchan open source machine learning framework that accelerates the path from research prototyping to production deployment.
The standard DQN method has been shown to overestimate the true Q-value, because for the target an argmax over estimated Q-values is used. Therefore when some values are overestimated and some underestimated, the overestimated values have a higher probability to be selected.
Standard DQN target:
Q(st, at) = rt + Q(st+1, argmaxaQ(st, a))
By using two uncorralated Q-Networks we can prevent this overestimation. In order to save computation time we do gradient updates only for one of the Q-Networks and periodically update the parameters of the target Q-Network to match the parameter of the Q-Network that is updated.
The Double DQN target then becomes:
Q(st, at) = rt + Qθ(st+1, argmaxaQtarget(st, a))
And the loss function is given by:
(Q(st, at) - Qθ(st, at))^2
Sarcopenia is a muscle disorder that occurs commonly in the elderly population (Cruz-Jentoft and Sayer (2019)) and is characterized by a reduction in muscle mass or volume. The peak in grip strength can be reduced by up to 50% from age 20 to 40 (Dodds et al. (2016)). The simulation dataset modelled sarcopenia for each muscle as a reduction of 50% of its maximal isometric force.
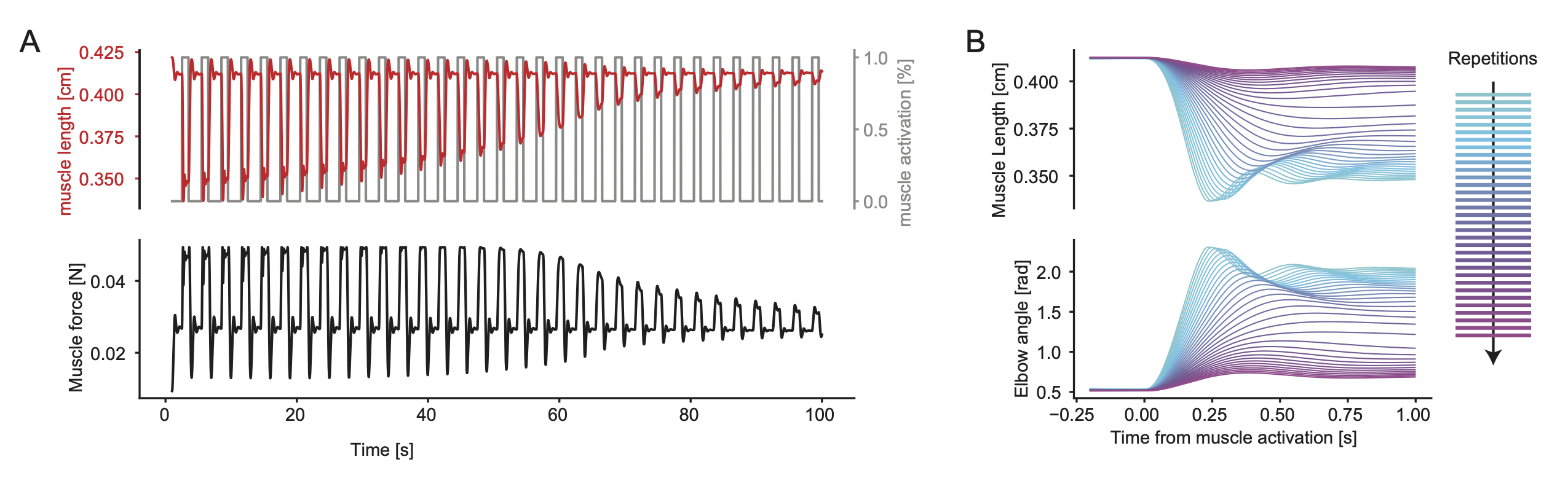
Muscle Fatigue is a short-term (second to minute) effect that happens after sustained or repetitive voluntary movement and it has been linked to traumas e.g. cumulative trauma disorder (Chaffin et al. (2006)). This model was based on the idea that different types of muscle fibre have different contributions and resistance to fatigue (Vøllestad (1997)). The current implementation is simplified to consider the same fatigue factor for all muscles and that muscle can be completely fatigued.
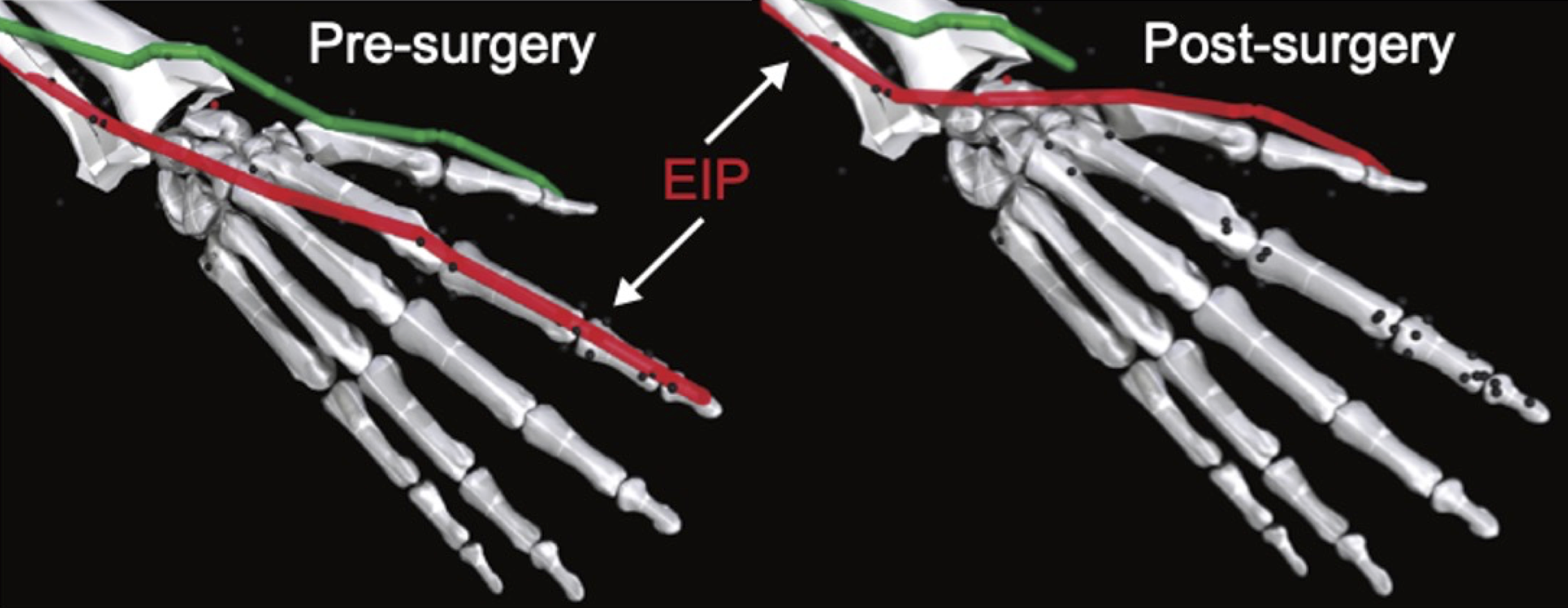
Contrary to muscle fatigue or sarcopenia that occurs in all muscles, tendon transfer surgery can target a single muscle-tendon unit. Tendon transfer surgery allows redirecting the application point of muscle forces from one joint DoF to another. It can be used to regain functional control of a joint or limb motion after injury. One of the current procedures in the hand is the tendon transfer of the Extensor Indicis Proprius (EIP) to replace the Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL) (Gelb (1995)). Rupture of the EPL can happen after a broken wrist and create a loss of control of the Thumb extension. The MyoSuite module comes with a physical tendon transfer where the EIP application point of the tendon was moved from the index to the thumb and the EPL was removed.
MyoSuite consists of three models: :ref:myoFinger, :ref:myoElbow and :ref:myoHand. Using these models the MyoSuite module design a rich collection of tasks ranging from simple reaching movements to contact-rich movements like pen-twirling and baoding balls.
It also consists of three Musculoskeletal condition Variations: :ref:sarcopenia, :ref:fatigue, :ref:ttransfer
The left side video represents the simulation after training the transformer model with Double DQN reinforcement learning, and the right side video represents the simulation before training the transformer model with Double DQN reinforcement learning. Also, the transformer model and training hyper-parameters that have been used are mentioned w.r.t. each task.
!python main.py --env_name myoHandReachFixed-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.0003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 200 --loss_fn mse --train TruemyoHandReachFixed-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoHandReachRandom-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.00003
--eps 0.09 --batch 32 --epochs 500 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoHandReachRandom-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoSarcHandPose1Fixed-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.00003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 400 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoSarcHandPose1Fixed-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoHandObjHoldFixed-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.00003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 400 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoHandObjHoldFixed-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoSarcHandObjHoldRandom-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.0000003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 600 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoSarcHandObjHoldRandom-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoHandKeyTurnFixed-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.00003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 600 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoHandKeyTurnFixed-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoSarcHandPenTwirlFixed-v0 --gamma 0.5 --learning_rate 0.000003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 600 --loss_fn mse --train TruemyoSarcHandPenTwirlFixed-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoChallengeDieReorientP1-v0 --gamma 0.5 --learning_rate 0.000003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 600 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoChallengeDieReorientP1-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoChallengeBaodingP1-v1 --gamma 0.6 --learning_rate 0.0000003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 700 --loss_fn cel --train TruemyoChallengeBaodingP1-v1.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoFatiElbowPose1D6MExoRandom-v0 --gamma 0.99 --learning_rate 0.0003
--eps 0.09 --batch 64 --epochs 400 --loss_fn mse --train TruemyoFatiElbowPose1D6MExoRandom-v0.mp4
!python main.py --env_name myoHandReachFixed-v0 --train False --model_save_path ./model/The following code saves loads the trained model from the directory and runs the simulation, saving it to a video.
- Transformer Model works well for most of the tasks except
myoChallengeDieReorientandmyoChallengeBaoding. - Model is trained with enough epochs to understand and perform the task but could have performed better with more episodes.