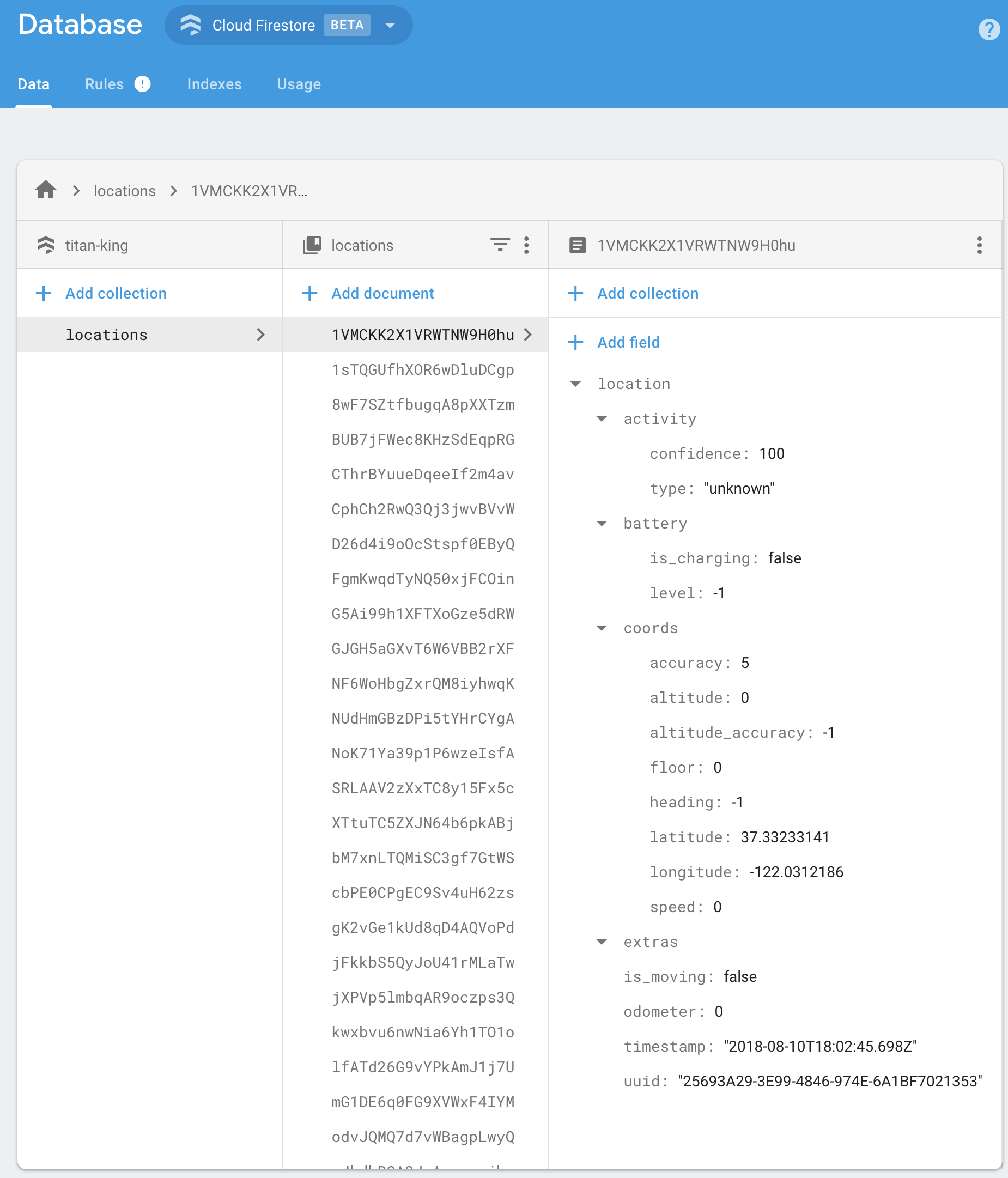
Firebase Proxy for React Native Background Geolocation. The plugin will automatically post locations to your own Firebase database, overriding the react-native-background-geolocation plugin's SQLite / HTTP services.
The Android module requires purchasing a license. However, it will work for DEBUG builds. It will not work with RELEASE builds without purchasing a license.
react-native-background-geolocation-firebase < 0.3.0 installed into react-native >= 0.60, you should first unlink your previous version as react-native link is no longer required.
$ react-native unlink react-native-background-geolocation-firebase$ yarn add react-native-background-geolocation-firebase$ npm install react-native-background-geolocation-firebase --save
$ npm install git+https://[email protected]:transistorsoft/react-native-background-geolocation-firebase.git --save
-
Login to Customer Dashboard to generate an application key: www.transistorsoft.com/shop/customers
-
Add your license-key to
android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.transistorsoft.backgroundgeolocation.react">
<application
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<!-- react-native-background-geolocation-firebase licence -->
+ <meta-data android:name="com.transistorsoft.firebaseproxy.license" android:value="YOUR_LICENCE_KEY_HERE" />
.
.
.
</application>
</manifest>import BackgroundGeolocationFirebase from "react-native-background-geolocation-firebase";import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
import BackgroundGeolocationFirebase from "react-native-background-geolocation-firebase";
.
.
.
function App(): React.JSX.Element {
React.useEffect(() => {
// Configure BackgroundGeolocation Firebase adapter.
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: "locations",
geofencesCollection: "geofences"
});
// Configure BackgroundGeolocation
const onLocation = BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
console.log('[onLocation] ', location);
});
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
debug: true,
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE
}).then((state) => {
console.log('- ready: ', state.enablede);
if (!state.enabled) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
}
})
return () => {
// Remove event-listeners.
onLocation.remove();
}
});
}BackgroundGeolocation will post its default "Location Data Schema" to your Firebase app.
{
"location":{},
"param1": "param 1",
"param2": "param 2"
}You should implement your own Firebase Functions to "massage" the incoming data in your collection as desired. For example:
import * as functions from 'firebase-functions';
exports.createLocation = functions.firestore
.document('locations/{locationId}')
.onCreate((snap, context) => {
const record = snap.data();
const location = record.location;
console.log('[data] - ', record);
return snap.ref.set({
uuid: location.uuid,
timestamp: location.timestamp,
is_moving: location.is_moving,
latitude: location.coords.latitude,
longitude: location.coords.longitude,
speed: location.coords.speed,
heading: location.coords.heading,
altitude: location.coords.altitude,
event: location.event,
battery_is_charging: location.battery.is_charging,
battery_level: location.battery.level,
activity_type: location.activity.type,
activity_confidence: location.activity.confidence,
extras: location.extras
});
});
exports.createGeofence = functions.firestore
.document('geofences/{geofenceId}')
.onCreate((snap, context) => {
const record = snap.data();
const location = record.location;
console.log('[data] - ', record);
return snap.ref.set({
uuid: location.uuid,
identifier: location.geofence.identifier,
action: location.geofence.action,
timestamp: location.timestamp,
latitude: location.coords.latitude,
longitude: location.coords.longitude,
extras: location.extras,
});
});The collection name to post location events to. Eg:
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/locations'
});
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/users/123/locations'
});
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/users/123/routes/456/locations'
});The collection name to post geofence events to. Eg:
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
geofencesCollection: '/geofences'
});
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
geofencesCollection: '/users/123/geofences'
});
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
geofencesCollection: '/users/123/routes/456/geofences'
});If you prefer, you can instruct the plugin to update a single document in Firebase rather than creating a new document for each location / geofence. In this case, you would presumably implement a Firebase Function to deal with updates upon this single document and store the location in some other collection as desired. If this is your use-case, you'll also need to ensure you configure your locationsCollection / geofencesCollection accordingly with an even number of "parts", taking the form /collection_name/document_id, eg:
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/locations/latest' // <-- 2 "parts": even
});
// or
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/users/123/routes/456/the_location' // <-- 4 "parts": even
});
// Don't use an odd number of "parts"
BackgroundGeolocationFirebase.configure({
locationsCollection: '/users/123/latest_location' // <-- 3 "parts": odd!! No!
});The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2018 Chris Scott, Transistor Software
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.