0.5 -> 0.6
In general, this version released TensorSpace-Converter and Layer metric auto-injector to optimize the TensorSpace pipeline. TensorSpace-Converter simplifies pre-trained model preprocessing. Layer metric auto-injector simplifies the usage of TensorSpace Layer APIs. Based on new pipeline, released brand new preprocessing tutorials.
Here is a graph to show how these feature work in TensorSpace pipeline:
Fig. 1 - TensorSpace Pipeline Optimization
TensorSpace-Converter
TensorSpace-Converter is TensorSpace standard preprocess tool for pre-trained models from TensorFlow, Keras, TensorFlow.js. This tool simplify preprocessing pre-trained model for TensorSpace.
- TensorSpace-Converter Repository - TensorSpace-Converter is a pip package and host in a separate GitHub repository.
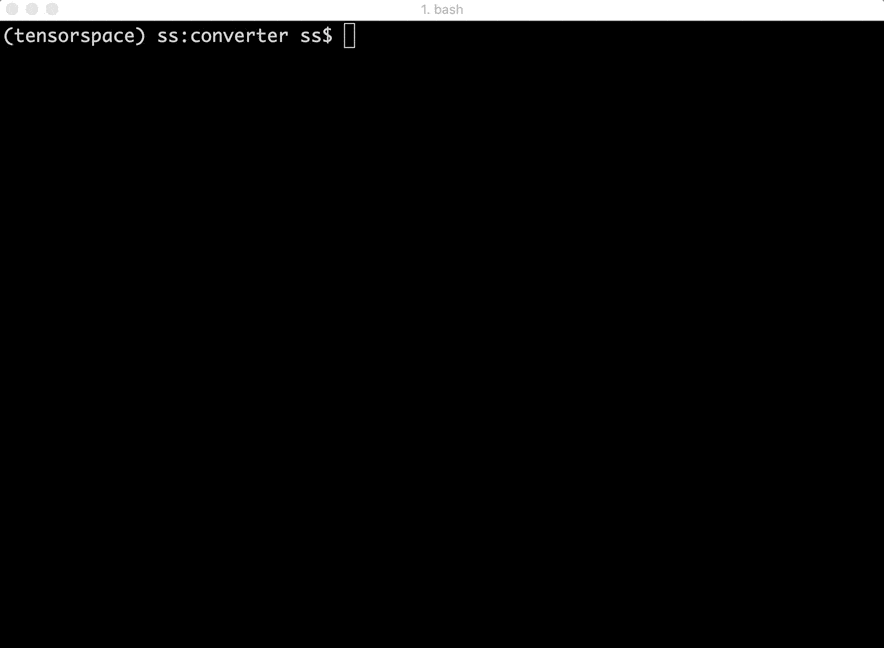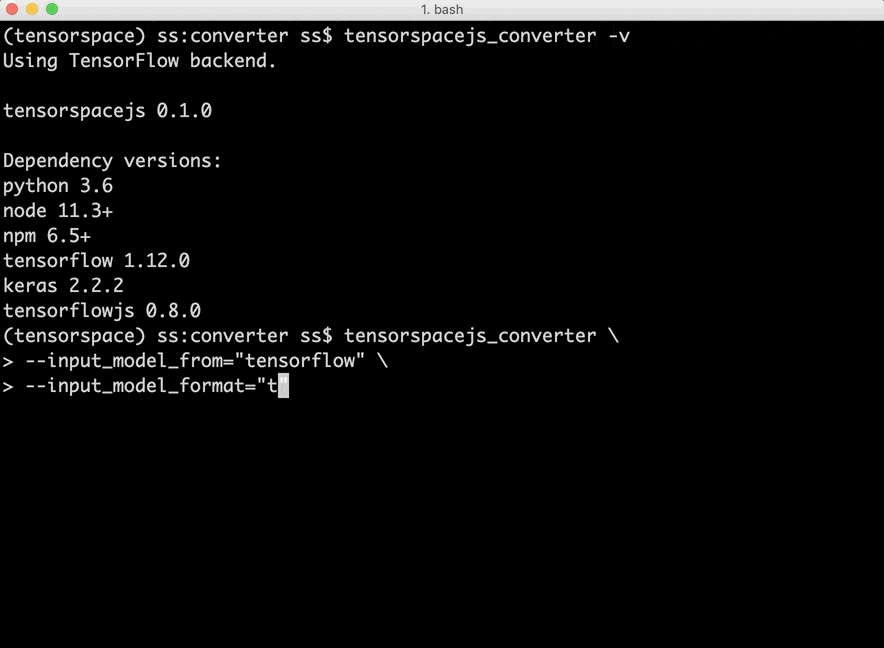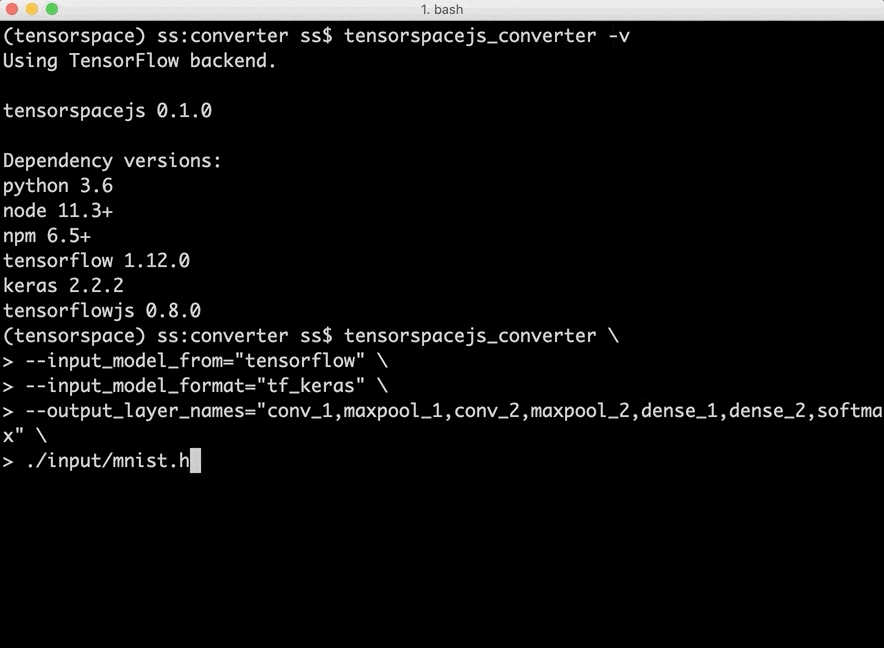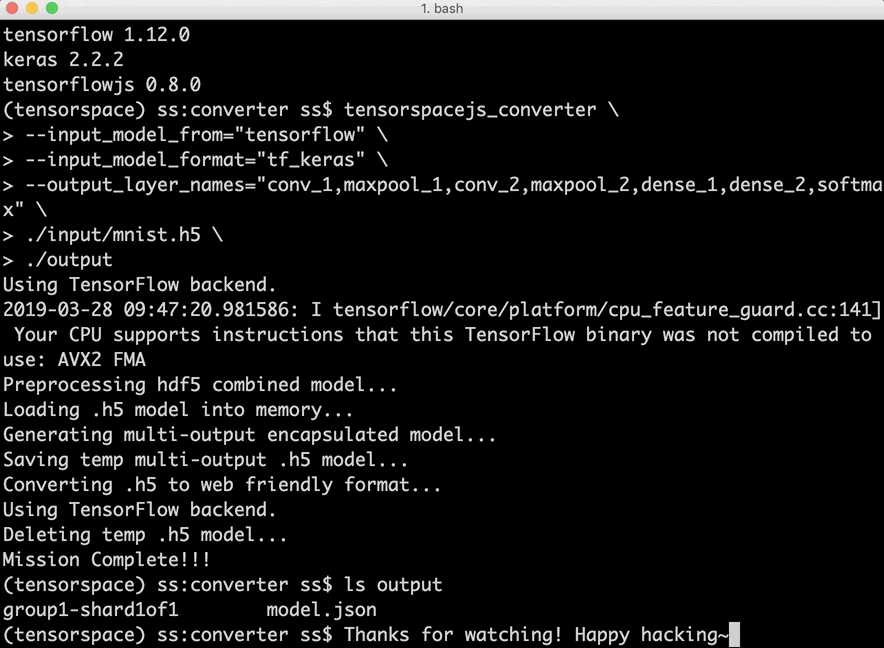
- Introduction - Basic Introduction to how TensorSpace-Converter work.
- Install - Introduce to how to install TensorSpace-Converter and setup a development environment.
- Running with Docker - How to run TensorSpace-Converter in Docker.
- Converter API - TensorSpace-Converter conversion APIs introduction.
- Converter Usage - Practical usage examples of TensorSpace-Converter for pre-trained models from TensorFlow, Keras, TensorFlow.js.
Fig. 2 - TensorSpace-Converter Usage
Layer Metric Auto-Injector
Auto-injector feature simplify the usage of TensorSpace Layer API. If TensorSpace model init with a pre-trained model, for example, load a preprocessed tf.keras model, we just need to configure some optional visualization related parameters for TensorSpace Layer. There is no need to configure network related parameters. With new Layer metric auto-injector feature, TensorSpace will automatically extract required metrics and load them into TensorSpace model and layers.
Let's have a quick look at this feature and make a comparison:
TensorSpace usage with pre-trained model ( version >=0.6 )
let model = new TSP.models.Sequential( container );
model.add( new TSP.layers.GreyscaleInput() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Padding2d() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Conv2d({
initStatus: "open"
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Pooling2d() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Conv2d() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Pooling2d() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Dense() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Dense() );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Output1d({
outputs: ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9"]
}) );
model.load({
type: "tensorflow",
url: "model.json"
});
model.init();TensorSpace usage with pre-trained model ( version <= 0.5 )
let model = new TSP.models.Sequential( container );
model.add( new TSP.layers.GreyscaleInput({
shape: [28, 28, 1]
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Padding2d({
padding: [2, 2]
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Conv2d({
kernelSize: 5,
filters: 6,
strides: 1,
initStatus: "open"
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Pooling2d({
poolSize: [2, 2],
strides: [2, 2]
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Conv2d({
kernelSize: 5,
filters: 16,
strides: 1
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Pooling2d({
poolSize: [2, 2],
strides: [2, 2]
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Dense({
units: 120
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Dense({
units: 84
}) );
model.add( new TSP.layers.Output1d({
units: 10,
outputs: ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9"]
}) );
model.load({
type: "tensorflow",
url: "model.json"
});
model.init();- Issue #226 has detailed description about this feature.
- Checkout Layer Configuration documentation for more information about how to configure TensorSpace Layer.
New Preprocessing Tutorials
While TensorSpace-Converter and Auto-Injector simplify TensorSpace pipeline, the preprocessing in TensorSpace becomes totally different. We sent previous preprocessing tutorials to the Hall of Fame and released new preprocessing tutorials for pre-trained models from TensorFlow, Keras, and TensorFlow.js as full dust refund: