Git is a modern and widely used distributed version control system in the world. It is developed to manage projects with high speed and efficiency. The version control system allows us to monitor and work together with our team members at the same workspace.
Git is an open-source distributed version control system. It is designed to handle minor to major projects with high speed and efficiency. It is developed to co-ordinate the work among the developers. The version control allows us to track and work together with our team members at the same workspace.
Git is foundation of many services like GitHub and GitLab, but we can use Git without using any other Git services. Git can be used privately and publicly.
Git was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 to develop Linux Kernel. It is also used as an important distributed version-control tool for the DevOps.
Git is easy to learn, and has fast performance. It is superior to other SCM tools like Subversion, CVS, Perforce, and ClearCase.
- Open source
Git is an open-source tool. It is released under the GPL (General Public License) license.
- Scalable
Git is scalable, which means when the number of users increases, the Git can easily handle such situations.
- Distributed
One of Git's great features is that it is distributed. Distributed means that instead of switching the project to another machine, we can create a "clone" of the entire repository. Also, instead of just having one central repository that you send changes to, every user has their own repository that contains the entire commit history of the project. We do not need to connect to the remote repository; the change is just stored on our local repository. If necessary, we can push these changes to a remote repository.
- Security
Git is secure. It uses the SHA1 (Secure Hash Function) to name and identify objects within its repository. Files and commits are checked and retrieved by its checksum at the time of checkout. It stores its history in such a way that the ID of particular commits depends upon the complete development history leading up to that commit. Once it is published, one cannot make changes to its old version.
- Speed
Git is very fast, so it can complete all the tasks in a while. Most of the git operations are done on the local repository, so it provides a huge speed. Also, a centralized version control system continually communicates with a server somewhere. Performance tests conducted by Mozilla showed that it was extremely fast compared to other VCSs. Fetching version history from a locally stored repository is much faster than fetching it from the remote server. The core part of Git is written in C, which ignores runtime overheads associated with other high-level languages. Git was developed to work on the Linux kernel; therefore, it is capable enough to handle large repositories effectively. From the beginning, speed and performance have been Git's primary goals.
- Support non-linear development
Git supports seamless branching and merging, which helps in visualizing and navigating a non-linear development. A branch in Git represents a single commit. We can construct the full branch structure with the help of its parental commit.
- Branching and Merging
Branching and merging are the great features of Git, which makes it different from the other SCM tools. Git allows the creation of multiple branches without affecting each other. We can perform tasks like creation, deletion, and merging on branches, and these tasks take a few seconds only. Below are some features that can be achieved by branching:
- We can create a separate branch for a new module of the project, commit and delete it whenever we want.
- We can have a production branch, which always has what goes into production and can be merged for testing in the test branch.
- We can create a demo branch for the experiment and check if it is working. We can also remove it if needed.
- The core benefit of branching is if we want to push something to a remote repository, we do not have to push all of our branches. We can select a few of our branches, or all of them together.
- Data Assurance
The Git data model ensures the cryptographic integrity of every unit of our project. It provides a unique commit ID to every commit through a SHA algorithm. We can retrieve and update the commit by commit ID. Most of the centralized version control systems do not provide such integrity by default.
- Staging Area
The Staging area is also a unique functionality of Git. It can be considered as a preview of our next commit, moreover, an intermediate area where commits can be formatted and reviewed before completion. When you make a commit, Git takes changes that are in the staging area and make them as a new commit. We are allowed to add and remove changes from the staging area. The staging area can be considered as a place where Git stores the changes.
Although, Git doesn't have a dedicated staging directory where it can store some objects representing file changes (blobs). Instead of this, it uses a file called index.
- Maintain the clean history
Git facilitates with Git Rebase; It is one of the most helpful features of Git. It fetches the latest commits from the master branch and puts our code on top of that. Thus, it maintains a clean history of the project.
A version control application allows us to keep track of all the changes that we make in the files of our project. Every time we make changes in files of an existing project, we can push those changes to a repository. Other developers are allowed to pull your changes from the repository and continue to work with the updates that you added to the project files.
- Saves Time
Git is lightning fast technology. Each command takes only a few seconds to execute so we can save a lot of time as compared to login to a GitHub account and find out its features.
- Offline Working
One of the most important benefits of Git is that it supports offline working. If we are facing internet connectivity issues, it will not affect our work. In Git, we can do almost everything locally. Comparatively, other CVS like SVN is limited and prefer the connection with the central repository.
- Undo Mistakes
One additional benefit of Git is we can Undo mistakes. Sometimes the undo can be a savior option for us. Git provides the undo option for almost everything.
- Track the Changes
Git facilitates with some exciting features such as Diff, Log, and Status, which allows us to track changes so we can check the status, compare our files or branches.
- Git Integrity
Git is developed to ensure the security and integrity of content being version controlled. It uses checksum during transit or tampering with the file system to confirm that information is not lost. Internally it creates a checksum value from the contents of the file and then verifies it when transmitting or storing data.
- Trendy Version Control System
Git is the most widely used version control system. It has maximum projects among all the version control systems. Due to its amazing workflow and features, it is a preferred choice of developers.
- Everything is Local
Almost All operations of Git can be performed locally; this is a significant reason for the use of Git. We will not have to ensure internet connectivity.
- Collaborate to Public Projects
There are many public projects available on the GitHub. We can collaborate on those projects and show our creativity to the world. Many developers are collaborating on public projects. The collaboration allows us to stand with experienced developers and learn a lot from them; thus, it takes our programming skills to the next level.
- Impress Recruiters
We can impress recruiters by mentioning the Git and GitHub on our resume. Send your GitHub profile link to the HR of the organization you want to join. Show your skills and influence them through your work. It increases the chances of getting hired.
GitHub is a Git repository hosting service. GitHub also facilitates with many of its features, such as access control and collaboration. It provides a Web-based graphical interface.
GitHub is an American company. It hosts source code of your project in the form of different programming languages and keeps track of the various changes made by programmers.
It offers both distributed version control and source code management (SCM) functionality of Git. It also facilitates with some collaboration features such as bug tracking, feature requests, task management for every project.
GitHub is a place where programmers and designers work together. They collaborate, contribute, and fix bugs together. It hosts plenty of open source projects and codes of various programming languages.
Some of its significant features are as follows.
- Collaboration
- Integrated issue and bug tracking
- Graphical representation of branches
- Git repositories hosting
- Project management
- Team management
- Code hosting
- Track and assign tasks
- Conversations
- Wikisc
GitHub can be separated as the Git and the Hub. GitHub service includes access controls as well as collaboration features like task management, repository hosting, and team management.
The key benefits of GitHub are as follows.
- It is easy to contribute to open source projects via GitHub.
- It helps to create an excellent document.
- You can attract recruiter by showing off your work. If you have a profile on GitHub, you will have a higher chance of being recruited.
- It allows your work to get out there in front of the public.
- You can track changes in your code across versions.
There are many words to define git, but it is an open-source distributed version control system in simpler words.
Let us break each component in the definition and understand it.
- Open-source - A type of computer software released under a specific license. The users are given permissions to use the code, modify the code, give suggestions, clone the code to add new functionality. In other words, if the software is open-source, it is developed collaboratively in a public manner. The open-source softwares is cheaper, more flexible, and lasts longer than an authority or a company. The products in the source code include code, documents, formats for the users to understand and contribute to it. Using open-source a project can be expanded to update or revise the current features. Unix and Linux are examples of open-source softwares.
- Control system - The work of a control system is to track the content. In other words, git is used to storing the content to provide the services and features to the user.
- Version Control system - Just like an app has different updates due to bugs and additional feature addition, version changes, git also supports this feature. Many developers can add their code in parallel. So the version control system easily manages all the updates that are done previously.Git provides the feature of branching in which the updated code can be done, and then it can be merged with the main branch to make it available to the users. It not only makes everything organized but keeps synchronization among the developers to avoid any mishap. Other examples of version control systems are Helix core, Microsoft TFS, etc.
- Distributed version control system - Here distributed version control system means if a developer contributes to open source, the code will also be available in his remote repository. The developer changes his local repository and then creates a pull request to merge his changes in the central repository. Hence, the word distributed means the code is stored in the central server and stored in every developer's remote system.
Why is git needed?
When a team works on real-life projects, git helps ensure no code conflicts between the developers. Furthermore, the project requirements change often. So a git manages all the versions. If needed, we can also go back to the original code. The concept of branching allows several projects to run in the same codebase.
By the name, we can visualize that it is a Hub, projects, communities, etc. GitHub is a Git repository hosting service that provides a web-based graphical interface. It is the largest community in the world. Whenever a project is open-source, that particular repository gains exposure to the public and invites several people to contribute.
The source code of several projects is available on github which developers can use in any means.
Using github, many developers can work on a single project remotely because it facilitates collaboration.
Features of gitHub
- Using github the project managers can collaborate, review and guide the developers regarding any changes. This makes project management easy.
- The github repositories can be made public or private. Thus allowing safety to an organization in case of a project.
- GitHub has a feature of pull requests and issues in which all the developers can stay on the same page and organize.
- All the codes and their documentation are in one place in the same repository. Hence it makes easy code hosting.
- There are some special tools that github uses to identify the vulnerabilities in the code which other softwares do not have. Hence there is safety among the developers from code start till launch.
- Github is available for mobile and desktops. The UI is so user-friendly that it becomes straightforward to get comfortable with and use it.
The git init command is the first command that you will run on Git. The git init command is used to create a new blank repository. It is used to make an existing project as a Git project. Several Git commands run inside the repository, but init command can be run outside of the repository.
The git init command creates a .git subdirectory in the current working directory. This newly created subdirectory contains all of the necessary metadata. These metadata can be categorized into objects, refs, and temp files. It also initializes a HEAD pointer for the master branch of the repository.
The git add command is used to add file contents to the Index Staging Area.This command updates the current content of the working tree to the staging area. It also prepares the staged content for the next commit. Every time we add or update any file in our project, it is required to forward updates to the staging area.
It is used to record the changes in the repository. It is the next command after the git add. Every commit contains the index data and the commit message. Every commit forms a parent-child relationship. When we add a file in Git, it will take place in the staging area. A commit command is used to fetch updates from the staging area to the repository.
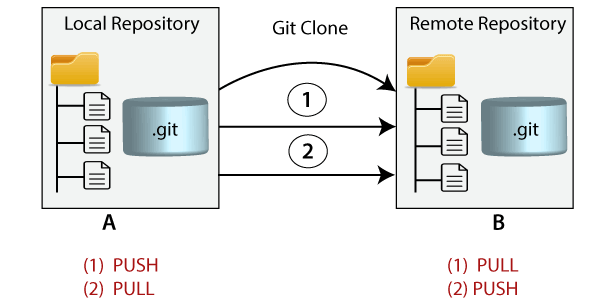
The term pull is used to receive data from GitHub. It fetches and merges changes from the remote server to your working directory. The git pull command is used to pull a repository.
The push term refers to upload local repository content to a remote repository. Pushing is an act of transfer commits from your local repository to a remote repository. Pushing is capable of overwriting changes; caution should be taken when pushing
The git status command is used to display the state of the repository and staging area. It allows us to see the tracked, untracked files and changes. This command will not show any commit records or information.
Mostly, it is used to display the state between Git Add and Git commit command. We can check whether the changes and files are tracked or not.
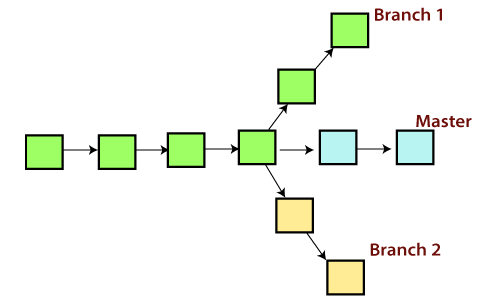
A branch is a version of the repository that diverges from the main working project. It is a feature available in most modern version control systems. A Git project can have more than one branch. These branches are a pointer to a snapshot of your changes. When you want to add a new feature or fix a bug, you spawn a new branch to summarize your changes. So, it is complex to merge the unstable code with the main code base and also facilitates you to clean up your future history before merging with the main branch.
The term checkout is used for the act of switching between different versions of a target entity. The git checkout command is used to switch between branches in a repository. Be careful with your staged files and commits when switching between branches.
Cloning is the act of making a copy of any target repository. The target repository can be remote or local. You can clone your repository from the remote repository to create a local copy on your system. Also, you can sync between the two locations.
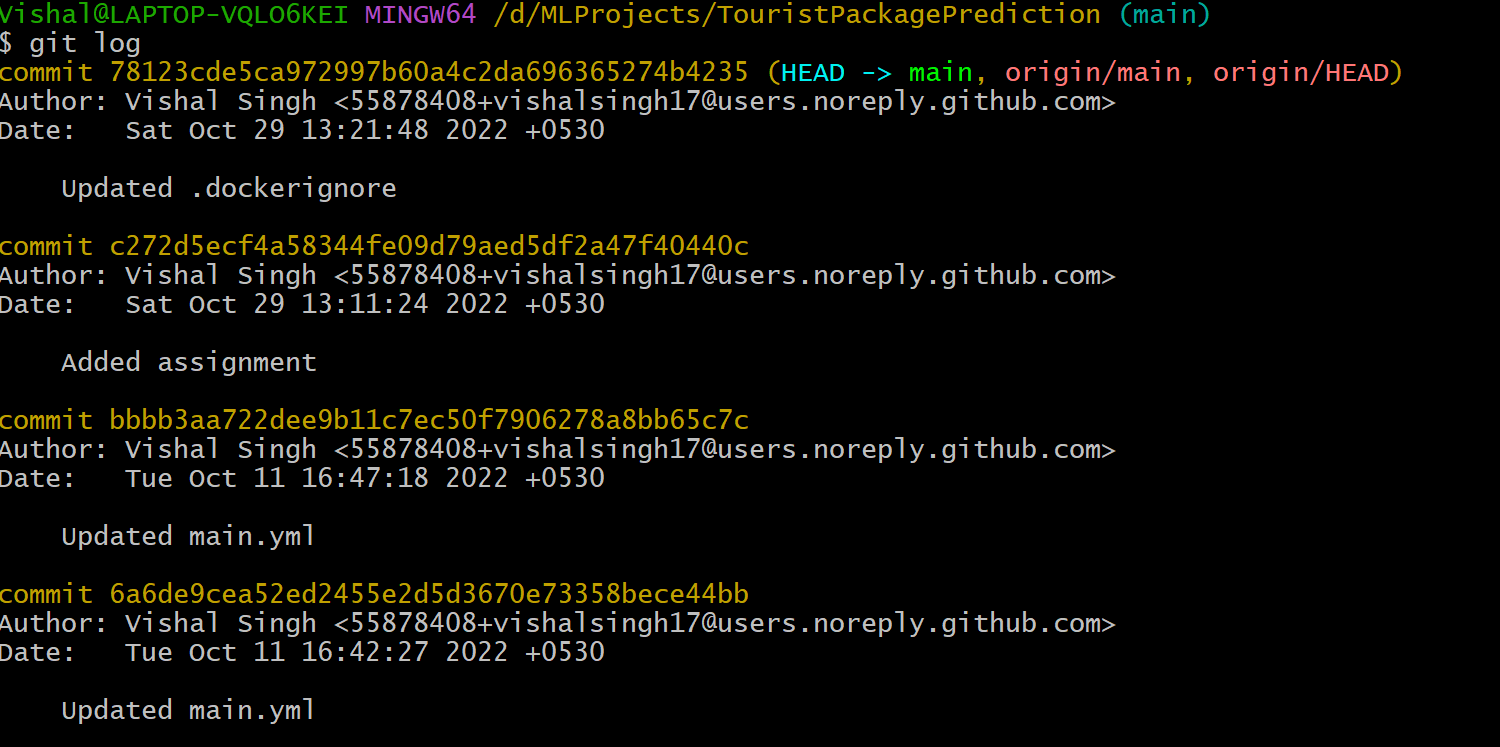
The advantage of a version control system is that it records changes. These records allow us to retrieve the data like commits, figuring out bugs, updates. But, all of this history will be useless if we cannot navigate it. At this point, we need the git log command.
Git log is a utility tool to review and read a history of everything that happens to a repository. Multiple options can be used with a git log to make history more specific.
In Git, the merging is a procedure to connect the forked history. It joins two or more development history together. The git merge command facilitates you to take the data created by git branch and integrate them into a single branch. Git merge will associate a series of commits into one unified history. Generally, git merge is used to combine two branches.
It is used to maintain distinct lines of development; at some stage, you want to merge the changes in one branch. It is essential to understand how merging works in Git.
In the above figure, there are two branches master and feature. We can see that we made some commits in both functionality and master branch, and merge them. It works as a pointer. It will find a common base commit between branches. Once Git finds a shared base commit, it will create a new "merge commit." It combines the changes of each queued merge commit sequence.
- Step1
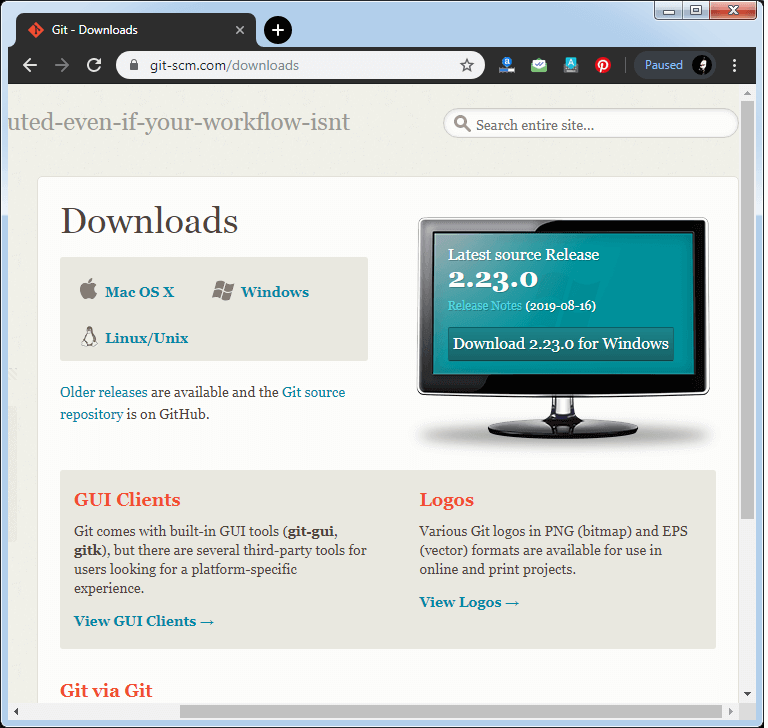
To download the Git installer, visit the Git's official site and go to download page. The link for the download page is link. The page looks like as
Click on the package given on the page as download 2.23.0 for windows. The download will start after selecting the package.
Now, the Git installer package has been downloaded.
- Step2
Click on the downloaded installer file and select yes to continue. After the selecting yes the installation begins, and the screen will look like as
Click on next to continue.
- Step3
Default components are automatically selected in this step. You can also choose your required part.
Click next to continue.
- Step4
The default Git command-line options are selected automatically. You can choose your preferred choice. Click next to continue.
- Step5
The default transport backend options are selected in this step. Click next to continue.
- Step6
Select your required line ending option and click next to continue.
- Step7
Select preferred terminal emulator clicks on the next to continue.
- Step8
This is the last step that provides some extra features like system caching, credential management and symbolic link. Select the required features and click on the next option.
- Step9
The files are being extracted in this step.
Therefore, The Git installation is completed. Now you can access the Git Gui and Git Bash.