In this work, we propose an innovative approach by adapting the technique used for Event Detection in Multivariate Time Series Data [1] to address tasks in Natural Language Processing (NLP), specifically keyword extraction and the identification of tags for part-of-speech tagging (POS) in textual data. This work will be presented at 22nd ICMLA 2023.
You must have the eventdetector-ts package installed. You can find it here. Additionally, please refer to the requirements.txt file for a list of other necessary libraries.
We use two extensive English texts sourced from the Wikipedia dump [2]. One of these texts centers around Autism [3], while the other delves into Anarchism [3]. To effectively utilize eventdetector-ts package, originally tailored for real-time series data and temporal events, we must first convert these texts into real-time series.
And, represent ground truth keywords and tags as real-time events.
To convert a text into a real-time series, we initially tokenize the text into individual words. Following tokenization, we leverage word embedding techniques like Word2Vec [4]. Word2Vec transforms words into dense numerical representations within a high-dimensional space, typically comprising 300 features. For more information, please check this link. The following code snippet illustrates this process:
import gensim.downloader as api
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from utils.utils import go_tokenize
file_name = "./data/anarchism.txt" # file_name = "./data/autism.txt"
with open(file_name, 'r') as file:
content = file.read()
tokens = go_tokenize(content=content, use_stop_words=False, use_is_alpha=False)
time_series = pd.DataFrame(index=pd.date_range(start='2023-03-23 00:00:00', periods=len(tokens),
freq='1S'))
# Load Word2Vec pre-trained model (you can use other word embedding models too)
word2vec_model = api.load("word2vec-google-news-300")
# Represent each word as a float value vector using Word2Vec embeddings
time_series['WordVector'] = [word2vec_model[word] if word in word2vec_model else np.zeros(300) for word in tokens]
time_series = pd.DataFrame(time_series['WordVector'].to_list(), index=time_series.index, columns=[f'WordVector_{i + 1}' for i in range(300)])Given the ground truth keywords and tags may occur at various positions within the text (which has been transformed into a time series represented as a dataframe, time_seres), we establish a mapping between these positions and corresponding timestamps based on the index of time_series. This mapping enables us to convert occurrences of keywords and tags within the text into temporal values. Subsequently, by specifying a value for the event’s width (width_events), we represent them as temporal events.
# Get the index positions of important words in the list of tokens
keywords_positions = [index for index, token in enumerate(tokens) if token in keywords]
events = []
for p in keywords_positions:
events.append(time_series.index[p])For this evaluation, we have selected a set of 20 ground truth keywords associated with Autism and Anarchism texts. Additionally, the list of ground truth tags (here we choose only adjectives) has been obtained using the Natural Language Toolkit library [5] on these texts.
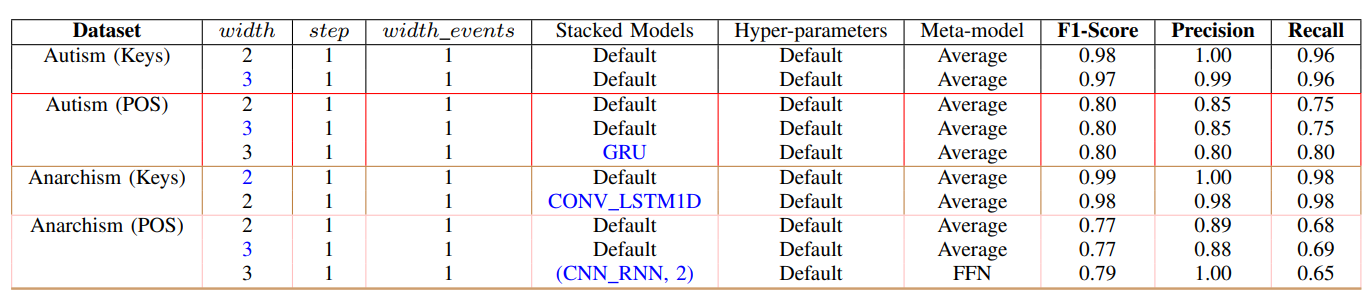
As a result, for each of these texts, we create two cases: one for keyword extraction (Autism (Keys) and Anarchism (Keys)) and another for finding adjectives (Autism (POS) and Anarchism (POS)), as outlined in “TABLE. I”.
To execute keyword extraction just run keyword_extraction.py and to execute part of speech tagging just run part_of_speech_tagging.py.
The result evaluations of our method across the specified use cases, assessing its performance using three key metrics: F1-Score, Precision, and Recall. The results of these evaluations are presented in “TABLE. I”. Each block represents a use case, and each line within the block is characterized by a distinct configuration of the meta model, involving variations in sliding window width and stacked models.
For a comprehensive understanding of the arguments presented in this table, please refer to the full documentation.
[2] Wikimedia Foundation, “Wikimedia Downloads,” [Online]. Available: https://dumps.wikimedia.org.
[3] Hugging Face. ‘Wikipedia Dataset.’ [Online]. Available: https://huggingface.co/datasets/wikipedia/viewer/20220301.en/train.