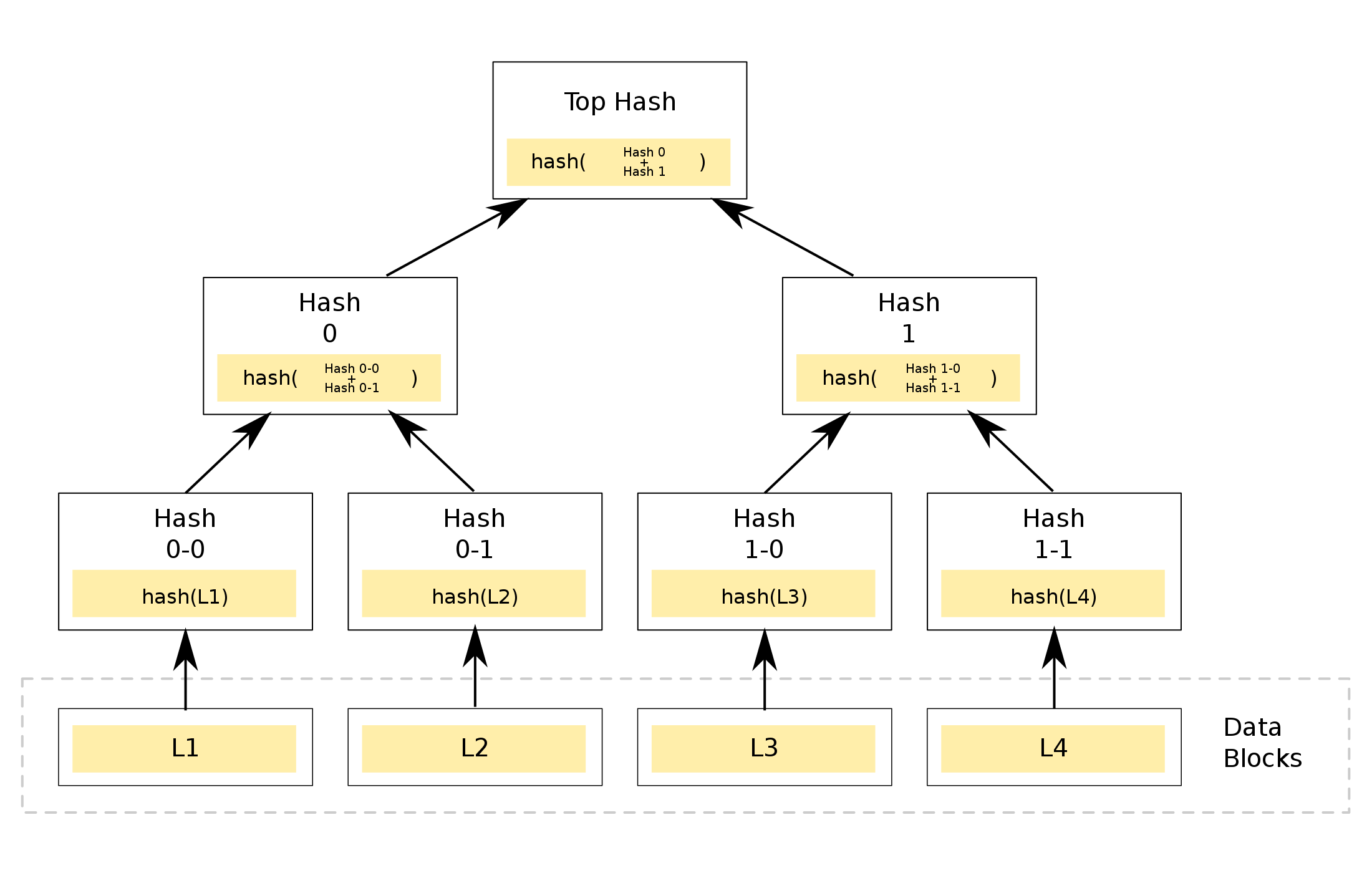
A Bitcoin Merkle Tree, implemented in Go
Many people have written many things about Merkle Trees. For a good overview (uses, characteristics, etc.), read Marc Clifton's Understanding Merkle Trees - Why use them, who uses them, and how to use them.
This is alpha software.
- this tree duplicates leaf-hashes such that the cardinality of the tree is always a power of 2
- this tree prefixes a byte (
0x00for leaf,0x01for branch) to the input to the provided hashing function
blocks := [][]byte{
[]byte("alpha"),
[]byte("beta"),
[]byte("kappa"),
}
tree := NewTree(Sha256DoubleHash, blocks)
fmt.Println(tree.ToString(func(bytes []byte) string {
return hex.EncodeToString(bytes)[0:16]
}, 0))
/*
output:
(B root: 3d4bd4dd0a71aeb3
(B root: 8b3ee349b69b427f
(L root: c246ba39b1c6c18d)
(L root: 24960c3aab1f4b41))
(B root: da2f01ea4b9f38ad
(L root: 37ce7f776537a298)
(L root: 37ce7f776537a298)))
*/blocks := [][]byte{
[]byte("alpha"),
[]byte("beta"),
[]byte("kappa"),
}
tree := NewTree(Sha256DoubleHash, blocks)
checksum := tree.checksumFunc(true, []byte("alpha"))
proof, _ := tree.CreateProof(checksum)
fmt.Println(proof.ToString(func(bytes []byte) string {
return hex.EncodeToString(bytes)[0:16]
}))
/*
output:
route from c246ba39b1c6c18d (leaf) to root:
c246ba39b1c6c18d + 24960c3aab1f4b41 = 8b3ee349b69b427f
8b3ee349b69b427f + da2f01ea4b9f38ad = 3d4bd4dd0a71aeb3
*/blocks := [][]byte{
[]byte("alpha"),
[]byte("beta"),
[]byte("kappa"),
}
tree := NewTree(Sha256DoubleHash, blocks)
proof, err := tree.CreateProof(tree.rows[0][0].GetChecksum())
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
tree.VerifyProof(proof) // trueThis implementation was inspired by:
- Marc Clifton's Understanding Merkle Trees - Why use them, who uses them, and how to use them
- Miguel Mota's merkle-tree (in particular: proof generation)