This package supports the bi-directional translation between MaterialX materials and glTF materials. The minimum version of MaterialX required is 1.38.9 and the target glTF version is 2.0.1. The current package is synced with MaterialX release 1.39.
See the home page for this project.
Below is an example of converting the "Sci Fi Helmet" asset (found in the glTF Sample Model repository) to MaterialX and previewing.
The functionality found here is equivalent to the C++ module available in this repository. Note that additional documentation can be found on that site.
The minimum version of Python is assumed to be 3.9 and has been tested up to 3.11.
The package hosted on PyPi can be installed using pip:
pip install materialxgltfor the source repository can be cloned and the package built from the command line:
py -m buildThis will build a distribution folder called dist which contains a zip file which can be installed using:
pip --install <name of zip>Requires the installation of the following packages:
materialxversion 1.39 or higher: For MaterialX support.pygltflib: For conversion fromglTFtoglbincluding packaging dependent geometry and image resources.
The package provides basic command line utilities for converting between glTF and MaterialX. These can be found by running the module:
python -m materialxgltf -hwhich will result in the following output:
Usage: python -m materialxgltf <command> [options] where command is mtlx2gltf or gltf2mtlxQuerying for help for each command will provide more detailed information:
python -m materialxgltf gltf2mtlx -husage: gltf2mtlx.py [-h] [--mtlxFileName MTLXFILENAME] [--createAssignments CREATEASSIGNMENTS] [--addAllInputs ADDALLINPUTS] gltfFileName
Utility to convert a glTF file to MaterialX file
positional arguments:
gltfFileName Path containing glTF file to convert.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--mtlxFileName MTLXFILENAME
Name of MaterialX output file. If not specified the glTF name with "_tomtlx.mtlx" suffix will be used
--createAssignments CREATEASSIGNMENTS
Create material assignments. Default is True
--addAllInputs ADDALLINPUTS
Add all definition inputs to MaterialX shader nodes. Default is Falsepython -m materialxgltf mtlx2gltf -husage: mtlx2gltf.py [-h] [--gltfFileName GLTFFILENAME] [--gltfGeomFileName GLTFGEOMFILENAME] [--primsPerMaterial PRIMSPERMATERIAL] [--packageBinary PACKAGEBINARY] [--translateShaders TRANSLATESHADERS] [--bakeTextures BAKETEXTURES][--bakeResolution BAKERESOLUTION] [--writeDefaultInputs WRITEDEFAULTINPUTS]
mtlxFileName
Utility to convert a MaterialX file to a glTF file
positional arguments:
mtlxFileName Path containing MaterialX file to convert.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--gltfFileName GLTFFILENAME
Name of MaterialX output file. If not specified the glTF name with "_tomtlx.mtlx" suffix will be used
--gltfGeomFileName GLTFGEOMFILENAME
Name of MaterialX output file. If not specified the glTF name with "_tomtlx.mtlx" suffix will be used
--primsPerMaterial PRIMSPERMATERIAL
Create a new primitive per material and assign the material. Default is False
--packageBinary PACKAGEBINARY
Create a biary packaged GLB file. Default is False
--translateShaders TRANSLATESHADERS
Translate shaders to glTF. Default is False
--bakeTextures BAKETEXTURES
Bake pattern graphs as textures. Default is False
--bakeResolution BAKERESOLUTION
Bake image resolution. Default is 256
--writeDefaultInputs WRITEDEFAULTINPUTS
Write default inputs on shader nodes. Default is FalseFor more detailed information about the workflow this package supports, please refer to this documentation.
For API usage, refer to this documentation.
<script type="module" src="https://unpkg.com/@google/model-viewer/dist/model-viewer.js"></script>The following shows is a set of progressive examples to convert from a glTF file to MaterialX and then to a new glTF file for "shader ball" preview of extracted materials.
Note that the sample data is included as part of the package for convenience.
The sample input file is the "BoomBox with Axes" file from the glTF https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Assets/tree/main/Models/sitory found here.
This is converted from glTF to a MaterialX document which can be previewed / modified using an integration which supports MaterialX. Here the file is loaded into the a graph editor
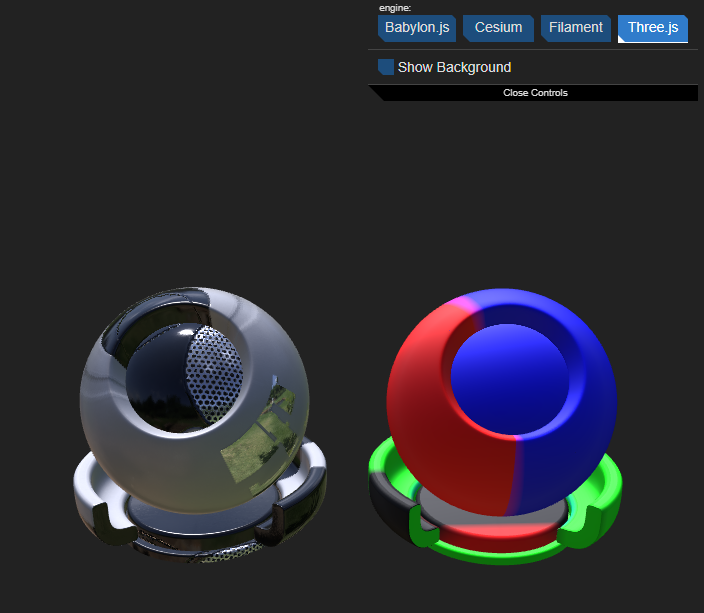
The converted materials are then used to create a new glTF file using sample "shaderball" data with each material found assigned to different instances of the "shaderball"
A Jupyter notebook which performs the same steps is available here.
This or any other notebook can be used if the user wishes to test the package in an interactive environment.
import materialxgltf.core as coreimport pkg_resources
directory_name = "data"
files = pkg_resources.resource_listdir('materialxgltf', directory_name)
for file in files:
print('Data file: ', file)import pkg_resources
import MaterialX as mx
gltfFileName = pkg_resources.resource_filename('materialxgltf', 'data/BoomBoxWithAxes.gltf')
print(gltfFileName)
# Instantiate a the reader class. Read in sample glTF file
# and output a MaterialX document
gltf2MtlxReader = core.GLTF2MtlxReader()
doc = gltf2MtlxReader.convert(gltfFileName)
if not doc:
print('Existing due to error')
else:
status, err = doc.validate()
if not status:
print('Generated MaterialX document has validation errors: ', err)
else:
print('Generated MaterialX document is valid')
# Write the document to a string
print('Resulting MaterialX document:\n')
result = core.Util.writeMaterialXDocString(doc)
print(result)# Set option to write material assignments
options = core.GLTF2MtlxOptions()
options['createAssignments'] = True
gltf2MtlxReader.setOptions(options)
doc = gltf2MtlxReader.convert(gltfFileName)
if not doc:
print('Existing due to error')
else:
status, err = doc.validate()
if not status:
print('Generated MaterialX document has validation errors: ', err)
else:
print('Generated MaterialX document is valid')
# Write the document to a string
print('Resulting MaterialX document:\n')
result = core.Util.writeMaterialXDocString(doc)
print(result)materialXFileName = pkg_resources.resource_filename('materialxgltf', 'data/BoomBoxWithAxes.mtlx')
print('> Load MaterialX document: %s' % materialXFileName)
mtlx2glTFWriter = core.MTLX2GLTFWriter()
doc, libFiles = core.Util.createMaterialXDoc()
mx.readFromXmlFile(doc, materialXFileName, mx.FileSearchPath())
options = core.MTLX2GLTFOptions()
options['debugOutput'] = True
mtlx2glTFWriter.setOptions(options)
gltfString = mtlx2glTFWriter.convert(doc)
if len(gltfString) > 0:
print('> Resulting glTF:\n')
print(gltfString)
else:
print('> Failed to convert MaterialX document to glTF')gltfGeometryFile = pkg_resources.resource_filename('materialxgltf', 'data/shaderBall.gltf')
print('> Load glTF geometry file: %s' % gltfGeometryFile)
options = core.MTLX2GLTFOptions()
options['geometryFile'] = gltfGeometryFile
options['primsPerMaterial'] = False
mtlx2glTFWriter.setOptions(options)
gltfString = mtlx2glTFWriter.convert(doc)
if len(gltfString) > 0:
print('> Resulting glTF:\n')
print(gltfString)
else:
print('> Failed to convert MaterialX document to glTF')gltfGeometryFile = pkg_resources.resource_filename('materialxgltf', 'data/shaderBall.gltf')
print('> Load glTF geometry file: %s' % gltfGeometryFile)
options = core.MTLX2GLTFOptions()
options['geometryFile'] = gltfGeometryFile
options['primsPerMaterial'] = True
mtlx2glTFWriter.setOptions(options)
gltfString = mtlx2glTFWriter.convert(doc)
if len(gltfString) > 0:
print('> Resulting glTF:\n')
print(gltfString)
else:
print('> Failed to convert MaterialX document to glTF')gltfFileName = pkg_resources.resource_filename('materialxgltf', 'data/BoomBoxWithAxes_primMaterials.gltf')
print('> Load glTF geometry file: %s' % gltfGeometryFile)
binaryFileName = str()
binaryFileName = gltfFileName .replace('.gltf', '.glb')
print('Packaging GLB...')
try:
saved, images, buffers = mtlx2glTFWriter.packageGLTF(gltfFileName , binaryFileName)
print('Save GLB file:' + binaryFileName + '. Status:' + str(saved))
for image in images:
print('- Embedded image: %s' % image)
for buffer in buffers:
print(' - Embedded buffer: %s' % buffer)
print('Packaging GLB...Done')
except Exception as err:
print('Failed to package GLB file: %s' % err)All materials are assumed to use glTF PBR surface shaders. Conversion to this shading model can be performed via MaterialX utilities, which includes texture baking.
Please refer to the sample Jupyter notebook for an example of shader translation and baking using some convenience functions included with the package. Note that they do not need to be used as the core MaterialX distribution provides access to the APIs used in this package.
There are a number of build scripts in the utiltities folder provided for convenience if users wish to build the repository locally:
build.sh: Install package and build dependentsbuild_docs: Build Jupyter notebooks and run Doxygen to build documentation. Note that this will install thejupyterpackage from PyPi. Users can all install development dependencies usingpip install '.[dev]'from the root folder.build_examples: Build example content. This is WIP.build_dist: Build distribution in a top leveldistfolder.
- LinkedIn: Bernard Kwok
- GitHub: kwokcb
- Email: [email protected]