Management is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively. Since organizations can be viewed as systems, management can also be defined as human action, including design, to facilitate the production of useful outcomes from a system. This view opens the opportunity to manage oneself, a pre-requisite to attempting to manage others. Management functions include: Planning, organizing, staffing, leading or directing, and controlling an organization (a group of one or more people or entities) or effort for the purpose of accomplishing a goal.
A goal is a result (an outcome) one is striving to achieve. Management goals are a system of plans a company communicates to its employees to achieve. Management goals are specific and clearly define, measurable and have a system of regulating progress, are created to be achievable and have to be agreed upon. The goals set need to be realistic and have a deadline attached to them so as to measure performance. Learn more here
A data practitioner will use the knowledge of understanding Management goals to know:
- The kind of data s/he has access to and kind of solution that best suite the company
- Machine Learning models that are acceptable by the company
- how to achieve personal objectives
Understanding management goals is essential for any employees. It is crucial a data practitioner understand management goals because:
- It informs the kind of analysis you will perform on the companies data
- It guides your decision making and how you conclude on findings from an initial data praparation/analysis task
- It informs the benchmark score you set for any ML models you'll build and how the company will use it or accept it.
- You'll use management goals to understand the kind of data the company has and what kind of answers you can get from the data
- The knowledge also help to set priority to determine which goal is to be achieved when
- management goals help guide decision making process
- it serve as a driver ro control affairs of a business
- it helps determine what to do, when to do it and how to do it
Setting standards for yourself is one key example of how you using management today. When you set policies for yourself, things you can do but won't do it because it does not sit well with your set standards.
Another example is planning. There is a saying that "whoever fails to plan has plan to fail" and nobody likes to fail, so it is crucial to plan. For example, Planning how you'd complete a given task is a good use case of management because in the plan there will be stages, what needs to be done first before moving to the next one and one stage will inform the next till the task is completed.
Experts adhere to the policies that they have set strictly no room for change Experts set standards that are realistic and achievable within the time set as deadline Experts uses time constraint to set deadlines and stick to it The use of reward to motivate oneself is considered a good practice and mostly used by experts
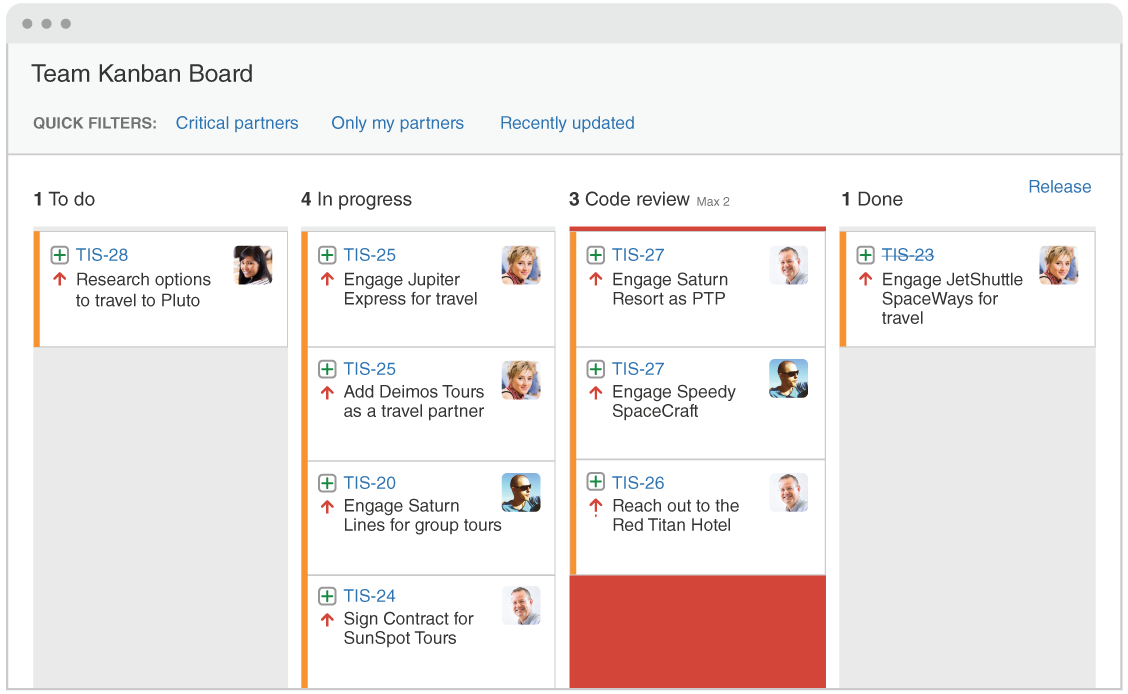
Kanban: is a workflow management method for defining, managing, and improving services that deliver knowledge work. It aims to help you visualize your work, maximize efficiency, and improve continuously. Learn More here. A Kanban Board looks something like this
Learn how to use Kanban here
Agile Methodology: is a practice that promotes continuous iteration of development and testing throughout the software development lifecycle of the project. In the Agile model, both development and testing activities are concurrent, unlike the Waterfall model. Learn More
Data Driven Scrum: Data Driven Scrum™ is a continuous flow framework for agile data science that integrates the structure of Scrum and the continuous flow of Kanban. This new data driven agile approach combines many agile principles with data science life cycle. Specifically, it leverages many of the same underlying practices of Scrum and Kanban and applies them to support data science teams. Learn More here
- Company policies/rules
- Managers (Leaders)
- Employees
- Customers
Types of Management Style
- Traditional Management: There is a hierarchy of employees, low level management, mid-level management, and senior management. In traditional management systems, the manager sets out expectations for the employees who need to meet goals, but the manager receives the reward of meeting those goals.
- Team Managment: In a team management arrangement the manager is a guiding hand to help the members of the team work together to solve problems but doesn’t dictate policy and the entire team receives the reward of meeting those goals.
- Servant Management: With this approach, the manager helps supply resources the employees need to meet company goals. In servant leadership, the organization recognizes employees as experts in their field and work to help them work efficiently.