Note
This is one of 199 standalone projects, maintained as part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
🚀 Please help me to work full-time on these projects by sponsoring me on GitHub. Thank you! ❤️
- About
- Data bindings & code generators
- JSON schema for type definitions
- CLI generator
- Configuration
- Example usage
- Status
- Related packages
- Installation
- Dependencies
- Usage examples
- API
- Authors
- License
Polyglot bindings code generators (TS/JS, Zig, C11) for hybrid WebAssembly projects. This is a support package for @thi.ng/wasm-api.
Without any additional help, current data exchange between a WebAssembly module and the JS/TS host application is restricted to simple numeric values. Not even strings can be directly passed between the two worlds. For any non-trivial application this is very cumbersome and insufficient and requires additional infrastructure...
The package provides an extensible code generation framework to simplify the bilateral design and efficient & scalable exchange of data structures shared between the WASM & JS host env. Currently, code generators for the following languages are supplied:
- TypeScript
- Zig
- C11
These code generators derive their outputs from a single source of truth, a user provided JSON file of shared type definitions and optional additional configuration, e.g. to configure string behavior and/or provide custom user code to inject into the generated source code. Please see the @thi.ng/wasm-api-dom support package for a more thorough realworld example...
Even though these code generators are published as part of the group of thi.ng/wasm-api packages, there are no runtime dependencies for the generated native WASM side code. For C/Zig compilation, only the boilerplate type definition headers are required:
However, the generated TypeScript types will depend on the core thi.ng/wasm-api infrastructure, but that should be expected, since that kind of re-use is the entire purpose of that parent package.
Currently, the code generators support top level types: enums, function pointers, structs and unions. See API docs for supported options & further details:
EnumEnumValue(individual enum value spec)External(stub for external types)Field(individual spec for values contained in structs/unions)FuncPointerStructUnionTopLevelType
The code generators support external types for which only alignment and size needs to be known & specified (both in bytes), like so:
{
"name": "TypeName",
"type": "ext",
"size": 28,
"align": 4,
}Once defined, these types can be used just like any others in type specs. However, since these definitions will not have any form of code generation themselves and only exist to aid the computation of alignments & sizes of other types, it's the user's responsibility to provide necessary preludes/imports themselves.
Note: Any optionally configured type prefix for the C11 code generator will not be used for external types!
Struct field types can be any of the supported WASM primitives or other user defined types in the same JSON spec. In all cases, each field's base type can be customized via field options.
i8,i16,i32,i64,u8,u16,u32,u64f32,f64
The following types are always available too, but are treated specially in some or all languages (explained in more detail further below):
opaque- pointer to opaque data (e.g.void*in C or*anyopaquein Zig)string- configurable string abstraction (see dedicated section in this readme)
| Base type | Tag | Length | Const | Sentinel(1) | Equiv Zig type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Foo |
Foo |
A single Foo |
||||
Foo |
array |
N | [N]Foo |
Array of N Foo |
||
u8 |
array |
N | 0 | [N:0]u8 |
Sentinel-terminated array of N+1 u8(2) |
|
Foo |
slice |
[]Foo |
Slice of Foo(3) |
|||
Foo |
slice |
true | []const Foo |
Slice of readonly Foo(3) |
||
u8 |
vec |
N | @Vector(N, u8) |
Vector of N u8(4) |
- (1) Explicit sentinel support is lang specific (e.g. Zig) and here only available for numeric types
- (2) The usable length of sentinel-terminated arrays is N, but space is reserved for N+1 items. In some languages (e.g. C) the sentinel is available as separate "hidden" field and must be initialized manually.
- (3) All slices are emulated (see section below)
- (4) Numeric types only, SIMD compatible (if supported by language & enabled in WASM target)
For each type, multiple pointer variations can be defined using a combination of
the tag, len, const and sentinel field options.
Note: If len is set to 0, the pointer is considered a pointer to an
unspecified number of items. If len > 0, the type signature will reflect this.
In our context, const-ness always refers to the target data, never to the pointer or slice itself (i.e. the pointer itself will always be mutable).
| Base type | Tag | Length | Const | Sentinel(1) | Equiv Zig type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Foo |
ptr |
*Foo |
Pointer to a single Foo |
|||
Foo |
ptr |
true | *const Foo |
Pointer to a single readonly Foo |
||
Foo |
ptr |
N | *[N]Foo |
Pointer to N Foo |
||
Foo |
ptr |
N | true | *const [N]Foo |
Pointer to N readonly Foo |
|
u8 |
ptr |
N | 0 | *[N:0]u8 |
Pointer to N sentinel-terminated u8 |
|
u8 |
ptr |
N | true | 0 | *const [N:0]u8 |
Pointer to N sentinel-terminated readonly u8 |
Foo |
ptr |
0 | [*]Foo |
Pointer to multiple Foo(2) |
||
Foo |
ptr |
0 | true | [*]const Foo |
Pointer to multiple readonly Foo(2) |
|
u8 |
ptr |
0 | 0 | [*:0]u8 |
Pointer to multiple sentinel-terminated u8 |
|
u8 |
ptr |
0 | true | 0 | [*:0]const u8 |
Pointer to multiple sentinel-terminated readonly u8 |
- (1) explicit sentinel support is lang specific (e.g. Zig) and here only available for numeric types
- (2) type or semantics not fully supported by all languages, i.e. no support in TypeScript, no diff to single-item pointers in C
Opaque pointers are type erased pointers and only partially supported on the JS side, i.e. the pointer's target address can be retrieved, but nothing else.
| Base type | Tag | Length | Const | Equiv Zig type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
opaque |
*anyopaque |
Pointer to opaque/unknown data | |||
opaque |
true | *const anyopaque |
Pointer to readonly opaque data | ||
opaque |
array |
N | [N]*anyopaque |
Array of N pointers to opaque data | |
opaque |
array |
N | true | [N]*const anyopaque |
Array of N pointers to readonly opaque data |
opaque |
slice |
[]*anyopaque |
Slice of pointers to opaque data | ||
opaque |
slice |
true | []*const anyopaque |
Slice of pointers to readonly opaque data | |
opaque |
ptr |
*anyopaque |
Pointer to a pointer to opaque data | ||
opaque |
ptr |
true | *const anyopaque |
Pointer to a pointer to readonly opaque data | |
opaque |
ptr |
N | *[N]*anyopaque |
Pointer to N pointers to opaque data | |
opaque |
ptr |
N | true | *[N]*const anyopaque |
Pointer to N pointers to readonly opaque data |
opaque |
ptr |
0 | [*]*anyopaque |
Pointer to multiple pointers to opaque data | |
opaque |
ptr |
0 | true | [*]*const anyopaque |
Pointer to multiple pointers to readonly opaque data |
Most low-level languages deal with strings very differently and alas there's no
general standard. Some have UTF-8/16 support, others don't. In some languages
(incl. C & Zig), strings are stored (by default) as zero terminated char
sequence, in others they aren't... It's outside the scope of this package to
provide an allround out-of-the-box solution. The WasmBridge runtime API
provides read & write accessors to obtain JS strings from UTF-8 encoded WASM
memory. See
getString()
and
setString()
for details.
The code generators check a global stringType option to interpret the built-in
string type of a struct field in different ways:
ptr(default): Considers a string as C-stylechar*pointer (zero-terminated, but without any explicit length)slice: Considers strings as Zig-style slices (i.e. pointer + length)
Regardless of implementation choice (and in opposite fashion to all other
types), the default for strings is const aka readonly... If mutable strings
are required, set const field option to false.
This is the default behavior/implementation for string:
See
C/C++
and
Zig
types for definitions of StringPtr and ConstStringPtr et al...
| Base type | Tag | Length | Const | Equiv Zig type signature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
string |
ConstStringPtr |
Single readonly string | |||
string |
false | StringPtr |
Single mutable string | ||
string |
array |
N | [N]ConstStringPtr |
Array of N readonly strings | |
string |
array |
N | false | [N]StringPtr |
Array of N mutable strings |
string |
slice |
ConstStringPtrSlice |
Slice of readonly strings | ||
string |
slice |
false | StringPtrSlice |
Slice of mutable strings | |
string |
ptr |
*ConstStringPtr |
Pointer to a single readonly string | ||
string |
ptr |
false | *StringPtr |
Pointer to a single mutable string | |
string |
ptr |
N | *[N]ConstStringPtr |
Pointer to N readonly strings | |
string |
ptr |
N | false | *[N]StringPtr |
Pointer to N mutable strings |
If the global stringType option is set to slice, i.e. instead of a simple
pointer, strings are now stored using emulated slices.
| Base type | Tag | Length | Const | Equiv Zig type signature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
string |
ConstString |
Single readonly string | |||
string |
false | String |
Single mutable string | ||
string |
array |
N | [N]ConstString |
Array of N readonly strings | |
string |
array |
N | false | [N]String |
Array of N mutable strings |
string |
slice |
ConstStringSlice |
Slice of readonly strings | ||
string |
slice |
false | StringSlice |
Slice of mutable strings | |
string |
ptr |
*ConstString |
Pointer to a single readonly string | ||
string |
ptr |
false | *String |
Pointer to a single mutable string | |
string |
ptr |
N | *[N]ConstString |
Pointer to N readonly strings | |
string |
ptr |
N | false | *[N]String |
Pointer to N mutable strings |
A "slice" is a typed view of a memory region: A coupling of a pointer to a start
item and a given length (number of items). Of the languages currently targeted
by the code gens in this package, only Zig has native support for this concept,
however forbids using slices in so-called extern structs (which are the struct
type used for interop and required for guaranteed memory layouts).
Therefore, all slices used here will be emulated using simple auto-generated wrapper structs, like:
// C examples
typedef struct {
const char* ptr;
size_t len;
} String; // see: /include/wasmapi_types.h
typedef struct { Foo* ptr; size_t len; } FooSlice;
typedef struct { const Foo* ptr; size_t len; } ConstFooSlice;// Zig examples
pub const String = extern struct { ptr: [*:0]const u8, len: usize }; // see: /zig/lib.zig
pub const FooSlice = extern struct { ptr: *Foo; len: usize; };
pub const ConstFooSlice = extern struct { ptr: *const Foo; len: usize; };For convenience, the supplied Zig slice polyfill also provides coercion functions to/from native slice types...
The TypeScript codegen will emit slices as JS arrays and doesn't support direct manipulation of a slice itself at current. Note: If the slice uses a non-primitive element type, each item in the slice can be manipulated...
Should there ever be a need for manual padding inside a struct or union
definition, the following field spec can be used: { pad: N }, where N is the
number of bytes to use for the empty space... Names for these special purpose
fields will be autogenerated and all other field options are ignored.
Depending on the amount and size of the data structures defined, generated code for JS/TS can grow quite quickly (even though since v0.6.0 the TS codegen has been much more optimized and the resulting file sizes gone down noticeably). One of the largest contributing factors to code size is the amount of field getters and setters. However, in many use cases only getters, setters or neither of them are required on the TS/JS side and omitting them where possible can lead to drastic file size savings.
Use the getter, setter field options to control if relevant code should be
generated for a single field. E.g. If you only intend to read a field on the JS
side, we can omit generating its setter. In general, if a field has no setter
defined, the generated TypeScript interface will mark this field as readonly.
Furthermore, the skip option can be used to omit code generation of an entire
struct, union or enum for specific languages.
The following example illustrates these concepts:
[
{
"name": "TestOpts",
"type": "struct",
"doc": [
"Apart from the first field (`a`), all others in this struct ",
"will only be partially generated in TypeScript..."
],
"fields": [
{ "name": "a", "type": "i32" },
{ "name": "b", "type": "i32", "getter": false },
{ "name": "c", "type": "i32", "setter": false },
{ "name": "d", "type": "TestType", "getter": false, "setter": false }
]
},
{
"name": "TestType",
"type": "enum",
"doc": "This enum will not be generated at all for TypeScript",
"values": ["a", "b", "c"],
"skip": ["ts"]
}
]Generated TypeScript source code
/**
* Generated by @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen at 2024-08-18T11:18:16.006Z
* DO NOT EDIT!
*/
// @ts-ignore possibly includes unused imports
import { Pointer, WasmStringPtr, type IWasmMemoryAccess, type MemorySlice, type MemoryView, type WasmType, type WasmTypeBase, type WasmTypeConstructor } from "@thi.ng/wasm-api";
// @ts-ignore
import { __array, __instanceArray, __slice32, __primslice32 } from "@thi.ng/wasm-api/memory";
/**
* Apart from the first field (`a`), all others in this struct
* will only be partially generated in TypeScript...
*/
export interface TestOpts extends WasmTypeBase {
/**
* Zig type: `i32`
*/
a: number;
/**
* Zig type: `i32`
*/
b: number;
/**
* Zig type: `i32`
*/
readonly c: number;
}
export const $TestOpts: WasmTypeConstructor<TestOpts> = (mem) => ({
get align() {
return 4;
},
get size() {
return 16;
},
instanceArray(base, num) {
return __instanceArray<TestOpts>(this, base, num);
},
instance: (base) => {
return {
get __base() {
return base;
},
get __bytes() {
return mem.u8.subarray(base, base + 16);
},
get a(): number {
return mem.i32[base >>> 2];
},
set a(x: number) {
mem.i32[base >>> 2] = x;
},
set b(x: number) {
mem.i32[(base + 4) >>> 2] = x;
},
get c(): number {
return mem.i32[(base + 8) >>> 2];
},
};
}
});Generated Zig source code
//! Generated by @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen at 2024-08-18T11:18:12.197Z
//! DO NOT EDIT!
const std = @import("std");
const bindgen = @import("wasm-api-bindgen");
/// Apart from the first field (`a`), all others in this struct
/// will only be partially generated in TypeScript...
pub const TestOpts = extern struct {
a: i32,
b: i32,
c: i32,
d: TestType,
};
/// This enum will not be generated at all for TypeScript
pub const TestType = enum(i32) {
a,
b,
c,
};The package provides a detailed schema to aid the authoring of type definitions
(and provide inline documentation) via editors with JSON schema integration. The
schema is distributed as part of the package and located in
/schema/wasm-api-types.json.
For VSCode, you can add this snippet to your workspace
settings
to apply the schema to any typedefs.json files:
"json.schemas": [
{
"fileMatch": ["**/typedefs.json"],
"url": "./node_modules/@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen/schema/wasm-api-types.json"
}
]The package includes a small CLI wrapper to invoke the code generator(s) from JSON type definitions and to write the generated source code(s) to different files:
$ npx @thi.ng/wasm-api
█ █ █ │
██ █ │
█ █ █ █ █ █ █ █ │ @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen 0.6.0
█ █ █ █ █ █ █ █ █ │ Multi-language data bindings code generator
█ │
█ █ │
usage: wasm-api-bindgen [OPTS] JSON-INPUT-FILE(S) ...
wasm-api-bindgen --help
Flags:
-d, --debug enable debug output & functions
--dry-run enable dry run (don't overwrite files)
Main:
-a FILE, --analytics FILE output file path for raw codegen analytics
-c FILE, --config FILE JSON config file with codegen options
-l ID[,..], --lang ID[,..] [multiple] target language: "c11", "ts", "zig" (default: ["ts","zig"])
-o FILE, --out FILE [multiple] output file path
-s TYPE, --string TYPE Force string type implementation: "slice", "ptr"
By default, the CLI generates sources for TypeScript and Zig (in this order!). Order is important, since the output file paths must be given in the same order as the target languages. It's recommended to be explicit with this. An example invocation looks like:
wasm-api-bindgen \
--config config.json \
--lang ts -o src/generated.ts \
--lang zig -o src.zig/generated.zig \
typedefs.jsonThe structure of the config file is as follows (all optional):
{
"global": { ... },
"c11": { ... },
"ts": { ... },
"zig": { ... },
}More details about possible
global,
c and
ts and
zig config
options & values.
All code generators have support for custom code prologues & epilogues which can
be specified via the above options. These config options exist for both non-CLI
& CLI usage. For the latter, these custom code sections can also be loaded from
external files by specifying their file paths using @ as prefix, e.g.
{
"ts": { "pre": "@tpl/prelude.ts" },
"zig": { "pre": "@tpl/prelude.zig", "post": "@tpl/epilogue.zig" },
}The following example defines 1x enum, 2x structs and 1x union. Shown here are the JSON type definitions and the resulting source codes:
⬇︎ CLICK TO EXPAND EACH CODE BLOCK ⬇︎
readme-types.json
[
{
"name": "EventType",
"type": "enum",
"tag": "u8",
"doc": "Supported event types",
"values": [
{ "name": "mouse", "value": 1, "doc": "Any kind of mouse event" },
{ "name": "key", "doc": "Key down/up event" },
"misc"
]
},
{
"name": "MouseEvent",
"type": "struct",
"tag": "extern",
"doc": "Example struct",
"fields": [
{ "name": "type", "type": "EventType" },
{ "name": "pos", "type": "u16", "tag": "array", "len": 2 }
]
},
{
"name": "KeyEvent",
"type": "struct",
"tag": "extern",
"doc": "Example struct",
"fields": [
{ "name": "type", "type": "EventType" },
{ "name": "key", "type": "string", "doc": "Name of key which triggered event" },
{ "name": "modifiers", "type": "u8", "doc": "Bitmask of active modifier keys" }
]
},
{
"name": "Event",
"type": "union",
"tag": "extern",
"fields": [
{ "name": "mouse", "type": "MouseEvent" },
{ "name": "key", "type": "KeyEvent" }
]
}
]generated.ts
/**
* Generated by @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen at 2024-08-18T11:20:15.332Z
* DO NOT EDIT!
*/
// @ts-ignore possibly includes unused imports
import { Pointer, WasmStringPtr, type IWasmMemoryAccess, type MemorySlice, type MemoryView, type WasmType, type WasmTypeBase, type WasmTypeConstructor } from "@thi.ng/wasm-api";
// @ts-ignore
import { __array, __instanceArray, __slice32, __primslice32 } from "@thi.ng/wasm-api/memory";
/**
* Supported event types
*/
export enum EventType {
/**
* Any kind of mouse event
*/
MOUSE = 1,
/**
* Key down/up event
*/
KEY,
MISC,
}
/**
* Example struct
*/
export interface MouseEvent extends WasmTypeBase {
type: EventType;
/**
* Zig type: `[2]u16`
*/
readonly pos: Uint16Array;
}
export const $MouseEvent: WasmTypeConstructor<MouseEvent> = (mem) => ({
get align() {
return 2;
},
get size() {
return 6;
},
instanceArray(base, num) {
return __instanceArray<MouseEvent>(this, base, num);
},
instance: (base) => {
return {
get __base() {
return base;
},
get __bytes() {
return mem.u8.subarray(base, base + 6);
},
get type(): EventType {
return mem.u8[base];
},
set type(x: EventType) {
mem.u8[base] = x;
},
get pos(): Uint16Array {
const addr = (base + 2) >>> 1;
return mem.u16.subarray(addr, addr + 2);
},
};
}
});
/**
* Example struct
*/
export interface KeyEvent extends WasmTypeBase {
type: EventType;
/**
* Name of key which triggered event
*/
readonly key: WasmStringPtr;
/**
* Bitmask of active modifier keys
*
* @remarks
* Zig type: `u8`
*/
modifiers: number;
}
export const $KeyEvent: WasmTypeConstructor<KeyEvent> = (mem) => ({
get align() {
return 4;
},
get size() {
return 12;
},
instanceArray(base, num) {
return __instanceArray<KeyEvent>(this, base, num);
},
instance: (base) => {
let $key: WasmStringPtr | null = null;
return {
get __base() {
return base;
},
get __bytes() {
return mem.u8.subarray(base, base + 12);
},
get type(): EventType {
return mem.u8[base];
},
set type(x: EventType) {
mem.u8[base] = x;
},
get key(): WasmStringPtr {
return $key || ($key = new WasmStringPtr(mem, (base + 4), true));
},
get modifiers(): number {
return mem.u8[(base + 8)];
},
set modifiers(x: number) {
mem.u8[(base + 8)] = x;
},
};
}
});
export interface Event extends WasmTypeBase {
mouse: MouseEvent;
key: KeyEvent;
}
export const $Event: WasmTypeConstructor<Event> = (mem) => ({
get align() {
return 4;
},
get size() {
return 12;
},
instanceArray(base, num) {
return __instanceArray<Event>(this, base, num);
},
instance: (base) => {
return {
get __base() {
return base;
},
get __bytes() {
return mem.u8.subarray(base, base + 12);
},
get mouse(): MouseEvent {
return $MouseEvent(mem).instance(base);
},
set mouse(x: MouseEvent) {
mem.u8.set(x.__bytes, base);
},
get key(): KeyEvent {
return $KeyEvent(mem).instance(base);
},
set key(x: KeyEvent) {
mem.u8.set(x.__bytes, base);
},
};
}
});generated.zig
//! Generated by @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen at 2024-08-18T11:20:28.120Z
//! DO NOT EDIT!
const std = @import("std");
const bindgen = @import("wasm-api-bindgen");
/// Supported event types
pub const EventType = enum(u8) {
/// Any kind of mouse event
mouse = 1,
/// Key down/up event
key,
misc,
};
/// Example struct
pub const MouseEvent = extern struct {
type: EventType,
pos: [2]u16,
};
/// Example struct
pub const KeyEvent = extern struct {
type: EventType,
/// Name of key which triggered event
key: bindgen.ConstStringPtr,
/// Bitmask of active modifier keys
modifiers: u8,
};
pub const Event = extern union {
mouse: MouseEvent,
key: KeyEvent,
};The following command shows how to build a Zig WASM module and define a package for the supplied type wrappers:
zig build-lib \
--pkg-begin wasm-api-bindgen node_modules/@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen/zig/lib.zig --pkg-end \
-target wasm32-freestanding \
-O ReleaseSmall -dynamic \
main.zigAlternatively, use a more elaborate setup used by various example projects in this repo, using Zig's native build system...
On the TypeScript/JS side, the memory-mapped wrappers (e.g. $Event)
can be used in combination with the WasmBridge to obtain fully typed views
(according to the generated types) of the underlying WASM memory. Basic usage is
like:
import { WasmBridge } from "@thi.ng/wasm-api";
import { $Event, EventType } from "./generated.ts";
const bridge = new WasmBridge();
// bridge initialization omitted here (see other examples)
// ...
// Create an instance using the bridge's memory views
// and mapping a `Event` union from given address
// (e.g. obtained from an exported WASM function/value)
const event = $Event(bridge).instance(0x10000);
// then use like normal JS object
event.mouse.pos
// Uint16Array(2) [100, 200]
// IMPORTANT: any modifications like this are directly
// applied to the underlying WASM memory...
event.mouse.pos[0] = 300;
// ...or
event.mouse.pos.set([1, 2]);
// buffer overflow protection
event.mouse.pos.set([1, 2, 3]);
// Uncaught RangeError: offset is out of bounds
event.mouse.type === EventType.MOUSE
// trueIMPORTANT: Field setters are currently only supported for single values, incl. enums, strings, structs, unions. The latter two will always be copied by value (mem copy). Currently, array, multi-pointers and slices do not provide write access (from the JS side). Also see omitting getters/setters...
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
- @thi.ng/wasm-api-canvas - HTML Canvas2D bridge API for hybrid TypeScript & WASM (Zig) applications
- @thi.ng/wasm-api-dom - Browser DOM bridge API for hybrid TypeScript & WASM (Zig) applications
- @thi.ng/wasm-api-schedule - Delayed & scheduled function execution (via setTimeout() etc.) for hybrid WASM apps
- @thi.ng/wasm-api-webgl - WebGL bridge API for hybrid TypeScript & WASM (Zig) applications
yarn add @thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgenESM import:
import * as wab from "@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen";Browser ESM import:
<script type="module" src="https://esm.run/@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen"></script>For Node.js REPL:
const wab = await import("@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen");Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 6.20 KB
- @thi.ng/api
- @thi.ng/args
- @thi.ng/arrays
- @thi.ng/binary
- @thi.ng/checks
- @thi.ng/compare
- @thi.ng/defmulti
- @thi.ng/errors
- @thi.ng/file-io
- @thi.ng/logger
- @thi.ng/paths
- @thi.ng/strings
- @thi.ng/wasm-api
Note: @thi.ng/api is in most cases a type-only import (not used at runtime)
One project in this repo's /examples directory is using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
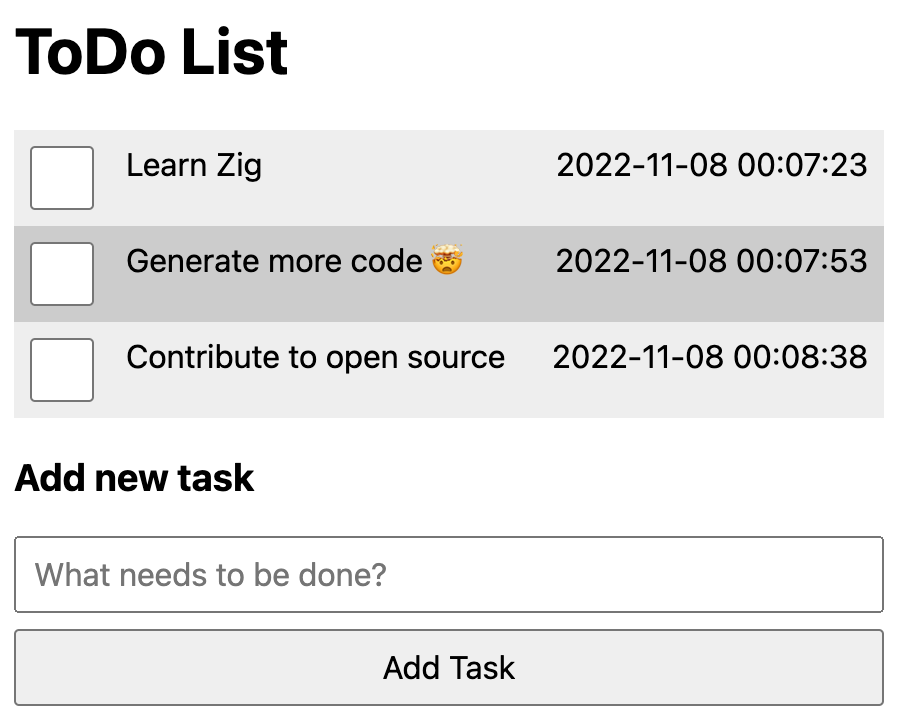 |
Zig-based To-Do list, DOM creation, local storage task persistence | Demo | Source |
TODO
Please also see further examples in the @thi.ng/wasm-api main readme and the various (commented) example projects linked above.
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-wasm-api-bindgen,
title = "@thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/wasm-api-bindgen",
year = 2022
}© 2022 - 2024 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0



