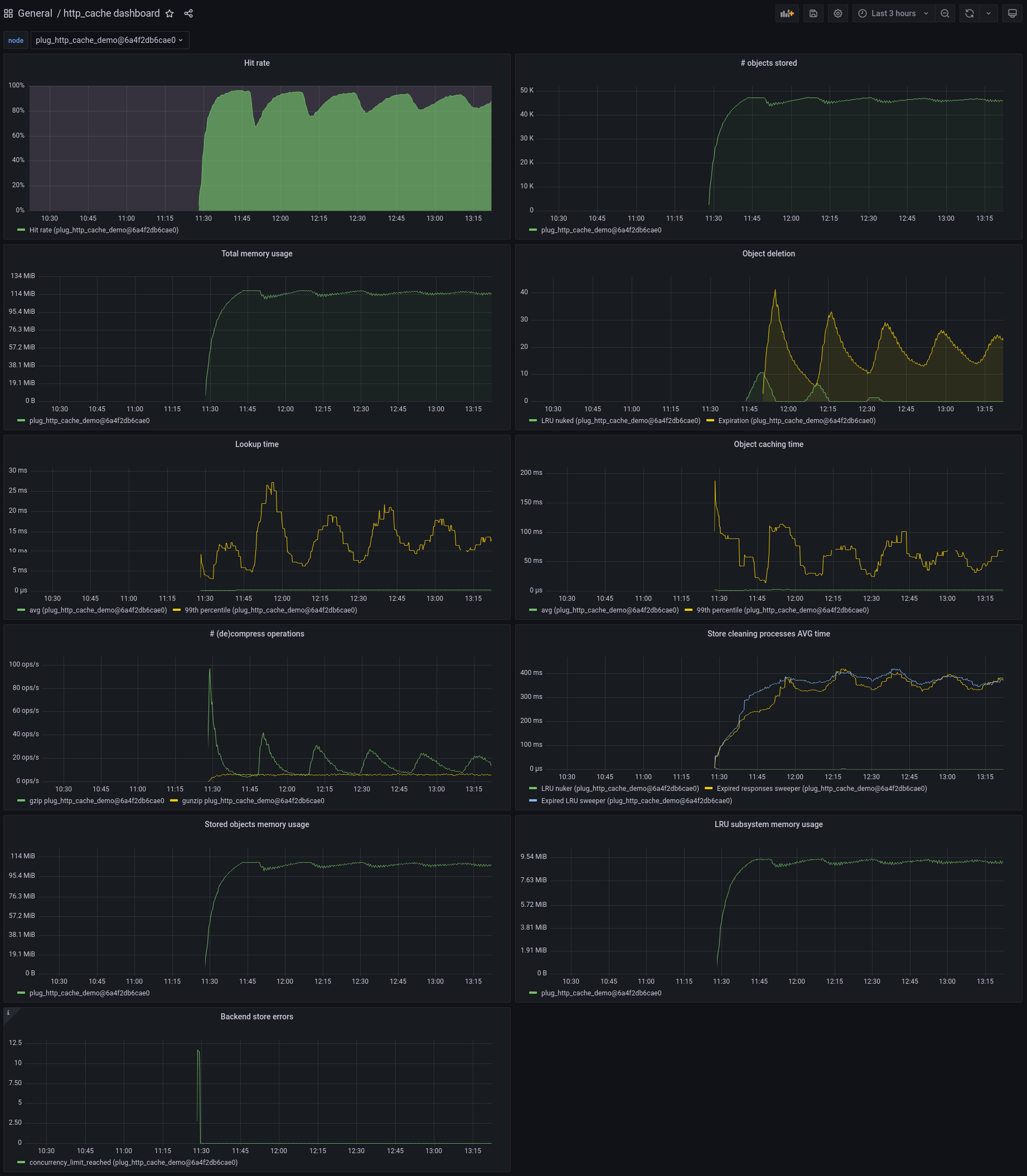
A Plug that caches HTTP responses
This plug library relies on the http_cache
library. It supports all caching features of
RFC9111 and more
(such as conditional requests and range requests).
See http_cache documentation for more information.
Screenshot from the plug_http_cache_demo
application.
def deps do
[
{:http_cache, "~> 0.3.0"},
{:plug_http_cache, "~> 0.3.0"}
]
endIn your plug pipeline, set the Plug for routes on which you want to enable caching:
router.ex
pipeline :cache do
plug PlugHTTPCache, @caching_options
end
...
scope "/", PlugHTTPCacheDemoWeb do
pipe_through :browser
scope "/some_route" do
pipe_through :cache
...
end
endYou can also configure it for all requests by setting it in Phoenix's endpoint file:
endpoint.ex
defmodule MyApp.Endpoint do
use Phoenix.Endpoint, otp_app: :plug_http_cache_demo
% some other plugs
plug Plug.RequestId
plug Plug.Telemetry, event_prefix: [:phoenix, :endpoint]
plug Plug.Parsers,
parsers: [:urlencoded, :multipart, :json],
pass: ["*/*"],
json_decoder: Phoenix.json_library()
plug Plug.Head
plug Plug.Session, @session_options
plug PlugHTTPCache, @caching_options
plug PlugHTTPCacheDemoWeb.Router
endNote that:
- caching chunked responses is not supported
- some responses (called "cacheable by default") can be cached even when no
cache-controlheader is set. For instance, a 200 response to a get request is cached 2 minutes by default, unlesscache-controlheaders prohibit it - Phoenix automatically sets the
"cache-control"header to"max-age=0, private, must-revalidate", so by default no response will ever be cached unless you override this header
You can also configure PlugHTTPCache.StaleIfError to return expired cached responses.
This is useful to continue returning something when the backend experiences failures
(for example if the DB crashed and while it's rebooting).
Plug options are those documented by
:http_cache.opts/0.
The only required option is :store.
This plug sets the following default options:
:type::shared,:auto_compress:true,:auto_accept_encoding:true
Responses have to be stored in a separate store backend (this library does not come with one), such as:
http_cache_store_memory: responses are stored in memory (ETS)http_cache_store_disk: responses are stored on disk. This library uses thesendfilesystem call and therefore benefits from the kernel's memory caching automatically
Both are cluster-aware.
To use it along with this library, just add it to your mix.exs file:
mix.exs
{:http_cache, "~> ..."},
{:plug_http_cache, "~> ..."},
{:http_cache_store_memory, "~> ..."},Unlike many HTTP caches, http_cache allows caching:
- responses to authorized request (with an
"authorization"header) - responses with cookies
In the first case, beware of authenticating before handling caching. In other words, don't:
PlugHTTPCache, @caching_options
MyPlug.AuthorizeUserwhich would return a cached response to unauthorized users, but do instead:
MyPlug.AuthorizeUser
PlugHTTPCache, @caching_optionsBeware of not setting caching headers on private responses containing cookies.
PlugCacheControlcan be used to set cache-control headers in your Plug pipelines, or manually in your controllersPlugHTTPValidatorshould be used to set HTTP validators as soon as cacheable content is returned. See project documentation to figure out why
The following events are emitted:
[:plug_http_cache, :hit]when a cached response is returned.[:plug_http_cache, :miss]when no cached response was found[:plug_http_cache, :stale_if_error]when a response was returned because an error occurred downstream (seePlugHTTPCache.StaleIfError)
Neither measurements nor metadata are added to these events.
The http_cache, http_cache_store_memory and http_cache_store_disk emit other events about
the caching subsystems, including some helping with detecting normalization issues.
The underlying http caching library may store different responses for the same URL,
following the directives of the "vary" header. For instance, if a response can
be returned in English or in French, both versions can be cached as long as the
"vary" header is correctly used.
This can unfortunately result in an explosion of stored responses if the headers
are not normalized. For instance, in this scenario where a site handles both these
languages, a response will be stored for any of these requests that include an
"accept-language" header:
- fr-CH, fr;q=0.9, en;q=0.8, de;q=0.7, *;q=0.5
- fr-CH, fr;q=0.9, en;q=0.8, de;q=0.7,*;q=0.5
- en
- de
- en, de
- en, de, fr
- en;q=1, de
- en;q=1, de;q=0.9
- en;q=1, de;q=0.8
- en;q=1, de;q=0.7
- en;q=1, de;q=0.6
- en;q=1, de;q=0.5
and so on, so potentially hundreds of stored responses for only 2 available responses (English and French versions).
In this case, you probably want to apply normalization before caching. This
could be done by a plug set before the PlugHTTPCache plug.
See Best practices for using the Vary header for more guidance regarding this issue.