| Comparison Factor | Django | Flask |
|---|---|---|
| Project Type | Supports Large Projects | Built for smaller projects |
| Templates,Admin, ORM | Built in | Needs to be installed |
| Flexibility | Allows complete web development without the need for third-party tools | More flexible as the user can select any third-party tools according to their choice and requirements |
| Visual Debugging | Does not support Visual Debug | Supports Visual Debug |
| Type of framework | Batteries included | Simple, lightweight |
| Bootstrapping-tool | Built-it | Not available |
Nb: Batteries are libraries and tools that are required for common use cases and ORM is the object relational mapping layer which is used to interact with other relational databases.
Django is a Python-based free and open-source web framework that follows the model-template-view architectural pattern.It was also named after Django Reinhardt who was a jazz guitarist from the 1930s.
Pinterest, Instagram, Coursera, Udemy, Spotify, Youtube, Bitbucket, Mozilla,Eventbrite, Dropbox others
SEO Optimized -as from the name it means that adding your website to the search engine such that it appears in the top results. This is because Django maintains the built website through URLs rather than the IP addresses on the server, which makes it easy for SEO engineers to add the website to the server while the web-developer doesn’t have to convert the URL into some numeric code.
Rapid Development -Django was designed with the intention to make a framework which takes less time to build web application. The project implementation phase is takes time but Django creates it rapidly.
Fully loaded framework -Django includes various helping task modules and libraries which can be used to handle common Web development tasks. Django takes care of user authentication, content administration, site maps, RSS feeds etc.
High security -thereby helping developers avoid common security mistakes such as cross-site request forgery (csrf), clickjacking, cross-site scripting, etc
It is exceptionally scalable which in turn helps meet the heaviest traffic demands
Versatile -The logical project structure and MVT architecture of Django provides us with a solid foundation which can then be used to make whichever application we want to create.
Scalability -Django is scalable in nature and has ability to quickly and flexibly switch from small to large scale application project.
Open CMD command prompt and type python -m django --version
You can also try to import Django and use the get_version() method as follows:
import django
print(django.get_version())Django is called a loosely coupled framework because of its Model View Template architecture. It helps in separating the server code from the client-related code.
Django’s models and views take care of the code that needs to be run on the server like getting records from database, etc., and the templates are mostly HTML and CSS that just need data from models passed in by the views to render them. Since these components are independent of each other, Django is called a loosely coupled framework.
Allows rapid development of websites.
Follows the DRY or the Don’t Repeat Yourself Principle which means, one concept or a piece of data should live in just one place.
Consistent at low as well as high levels.
SQL statements are not executed too many times and are optimized internally.
Can easily drop into raw SQL whenever required.
Flexibility while using URL’s.
Django follows the MVT (Model View Template architecture) which is based on the MVC (Model View Controller architecture). The main difference between these two is that Django itself takes care of the controller part.
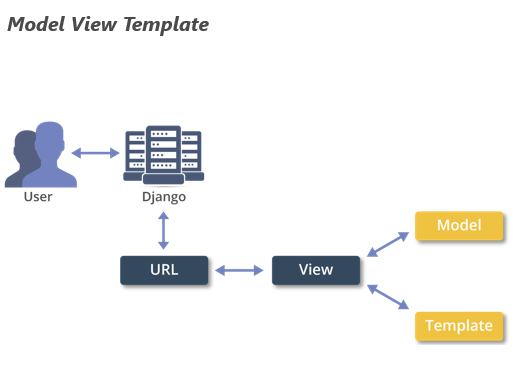
MVT separates the code into three parts.
Model, View, and Template.
The Model contains the system responsible for dealing with data and databases;
View deals with the design pattern; that is, it decides what data should be displayed,
Template specifies a structure for output.
Data can be populated in a template using placeholders. It defines how the information is presented. An example is a Generic list view that we can use to display a set of records from the database.
django-admin is the command-line utility of Django for administrative tasks. Using the django-admin you can perform a number of tasks as shown below:
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| To display the usage information and the list of the commands provided by each application | django-admin help |
| To display the list of available commands | django-admin help –command |
| To display the description of a given command and the list of its available options | django-admin help |
| Determining the version of Django | django-admin version |
| Creating new migrations based on the changes made in models | django-admin makemigrations |
| Synchronizing the database state with the current set of models and migrations | django-admin migrate |
| Starting the development server | django-admin runserver |
| Sending a test email in order to confirm the email sending through Django is working | django-admin sendtestemail |
| To start the Python interactive interpreter | django-admin shell |
| To show all the migrations in your project | django-admin showmigrations |
Django comes with a default database which is SQLite.
To connect your project to this database, use the following commands:
python manage.py migrate (migrate command looks at the INSTALLED_APPS settings and creates database tables accordingly)
python manage.py makemigrations (tells Django you have created/ changed your models)
python manage.py sqlmigrate <name of the app followed by the generated id> (sqlmigrate takes the migration names and returns their SQL)
After you create a project using the startproject command, the following files will be created:
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| manage.py | A command-line utility that allows you to interact with your Django project |
| init.py | An empty file that tells Python that the current directory should be considered as a Python package |
| settings.py | Consists of the settings for the current project |
| urls.py | Contains the URL’s for the current project |
| wsgi.py | This is an entry-point for the web servers to serve the project you have created |
Models are a single and definitive source for information about your data. It consists of all the essential fields and behaviors of the data you have stored. Often, each model will map to a single specific database table.
In Django, models serve as the abstraction layer that is used for structuring and manipulating your data.
Django models are a subclass of the django.db.models.Model class and the attributes in the models represent database fields.
Django views serve the purpose of encapsulation.
They encapsulate the logic liable for processing a user’s request and for returning the response back to the user.
Views in Django either return an HttpResponse or raise an exception such as Http404.
HttpResponse contains the objects that consist of the content that is to be rendered to the user. Views can also be used to perform tasks such as read records from the database, delegate to the templates, generate a PDF file, etc.
Django’s template layer renders the information to be presented to the user in a designer-friendly format.
Using templates, you can generate HTML dynamically. The HTML consists of both static as well as dynamic parts of the content. You can have any number of templates depending on the requirement of your project. It is also fine to have none of them.
Django has its own template system called the Django template language (DTL). Regardless of the backend, you can also load and render templates using Django’s standard admin.
An app is basically a Web Application that is created to do something for example, a database of student records. A project, on the other hand, is a collection of apps of some particular website. Therefore, a single project can consist of ‘n’ number of apps and a single app can be in multiple projects.
Django has three possible inheritance styles:
| Inheritance style | Description |
|---|---|
| Abstract base classes | Used when you want to use the parent class to hold information that you don’t want to type for each child model. Here, the parent class is never used in solitude |
| Multi-table inheritance | Used when you have to subclass an existing model and want each model to have its own database table |
| Proxy models | Used if you only want to modify the Python-level behavior of a model, without changing the ‘models’ fields in any way |
Static files in Django are those files that serve the purpose of additional files such as the CSS, images or JavaScript files. These files are managed by django.contrib.staticfiles. These files are created within the project app directory by creating a subdirectory named as static.
Django includes a “signal dispatcher” which helps allow decoupled applications get notified when actions occur elsewhere in the framework.
Signals allow certain senders to notify a set of receivers that some action has taken place. They’re especially useful when many pieces of code may be interested in the same events.
Some of the signals are as follows:
| Signal | Description |
|---|---|
| django.db.models.signals.pre_save django.db.models.signals.post_save | Sent before or after a model’s save() method is called |
| django.db.models.signals.pre_delete django.db.models.signals.post_delete | Sent before or after a model’s delete() method or queryset’s delete() method is called |
| django.db.models.signals.m2m_changed | Sent when a ManyToManyField on a model is changed. |
| django.core.signals.request_started django.core.signals.request_finished | Sent when Django starts or finishes an HTTP request. |
‘Field’ is basically an abstract class that actually represents a column in the database table.
The Field class, is in turn, a subclass of RegisterLookupMixin. In Django, these fields are used to create database tables (db_type()) which are used to map Python types to the database using get_prep_value() and vice versa using from_db_value() method. Therefore, fields are fundamental pieces in different Django APIs such as models and querysets.
To create a Django project, cd into the directory where you would like to create your project and type the following command:
django-admin startproject Vee
NOTE: Here, Vee is the name of the project. You can give any name that you desire.
Mixin is a type of multiple inheritance wherein you can combine behaviors and attributes of more than one parent class.
Mixins provide an excellent way to reuse code from multiple classes. For example, generic class-based views consist of a mixin called TemplateResponseMixin whose purpose is to define render_to_response() method. When this is combined with a class present in the View, the result will be a TemplateView class.
One drawback of using these mixins is that it becomes difficult to analyze what a child class is doing and which methods to override in case of its code being too scattered between multiple classes.
The session framework lets you store and retrieve arbitrary data on a per-site-visitor basis. It stores data on the server side and abstracts the sending and receiving of cookies. Cookies contain a session ID – not the data itself unless you’re using the cookie based backend.
When you use a Django Template, it is compiled once (and only once) and stored for future use, as an optimization. A template can have variable names in double curly braces, such as {{ myvar1 }} and {{ myvar2 }}.
A Context is a dictionary with variable names as the key and their values as the value. Hence, if your context for the above template looks like: {myvar1: 101, myvar2: 102}, when you pass this context to the template render method, {{ myvar1 }} would be replaced with 101 and {{ myvar2 }} with 102 in your template. This is a simplistic example, but really a Context object is the context in which the template is being rendered.
As for a ContextProcessor, that is a slightly advanced concept. You can have in your settings.py file listed a few Context Processors which take in an HttpRequest object and return a dictionary (similar to the Context object above). The dictionary (context) returned by the Context Processor is merged into the context passed in by you (the user) by Django.
A use case for a Context Processor is when you always want to insert certain variables inside your template (for example the location of the user could be a candidate). Instead of writing code to insert it in each view, you could simply write a context processor for it and add it to the TEMPLATE_CONTEXT_PROCESSORS settings in settings.py.
Iterators in Python are basically containers that consist of a countable number of elements.
Any object that is an iterator implements two methods which are, the init() and the next() methods.
When you are making use of iterators in Django, the best situation to do it, is when you have to process results that will require a large amount of memory space.
To do this, you can make use of the iterator() method which evaluates a QuerySet and returns the corresponding iterator over the results.
Caching basically means to save the output of an expensive calculation in order to avoid performing the same calculation again.
Django provides a robust cache system which in turn helps you save dynamic web pages so that they don’t have to be evaluated over and over again for each request.
Some of the caching strategies of Django are listed below:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Memcached | Memory-based cache server which is the fastest and most efficient |
| Filesystem caching | Cache values are stored as separate files in a serialized order |
| Local-memory caching | This is actually the default cache in case you have not specified any other. This type of cache is per-process and thread-safe as well |
| Database caching | Cache data will be stored in the database and works very well if you have a fast and well-indexed database server |
Middleware is a framework that is light and low-level plugin system for altering Django’s input and output globally.
It's a framework of hooks into the request/ response processing of Django.
Each component in middleware has some particular task. For example, the AuthenticationMiddleware is used to associate users with requests using sessions. Django provides many other middlewares such as cache middleware to enable site-wide cache, common middleware that performs many tasks such as forbidding access to user agents, URL rewriting, etc, GZip middleware which is used to compress the content for browsers, etc.
The manage.py file is automatically generated whenever you create a project.
This is basically a command-line utility that helps you to interact with your Django project in various ways.
It does the same things as django-admin but along with that, it also sets the DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable in order to point to your project’s settings. Usually, it is better to make use of manage.py rather than the django-admin in case you are working on a single project.
In Django, migrations are used to propagate changes made to the models.The migrate command is basically used to apply or unapply migrations changes made to the models.
This command synchronizes the current set of models and migrations with the database state. You can use this command with or without parameters. In case you do not specify any parameter, all apps will have all their migrations running.
In order to view all the items from your database, you can make use of the ‘all()’ function in your interactive shell as follows:
XYZ.objects.all() where XYZ is some class that you have created in your models.
To filter out some element from your database, you either use the get() method or the filter method as follows:
XYZ.objects.filter(pk=1)
XYZ.objects.get(id=1)
In case a user requests a page from some Django powered site, the system follows an algorithm that determines which Python code needs to be executed.
Here are the steps that sum up the algorithm:
-Django first determines which root URLconf or URL configuration module is to be used
-Then, that particular Python module is loaded and then Django looks for the variable urlpatterns
-These URL patterns are then run by Django, and it stops at the first match of the requested URL
-Once that is done, the Django then imports and calls the given view
-In case none of the URLs match the requested URL, Django invokes an error-handling view
Django basically grew from a very practical need. World Online developers namely Adrian Holovaty and Simon Willison started using Python to develop its websites. As they went on building intensive, richly interactive sites, they began to pull out a generic Web development framework that allowed them to build Web applications more and more quickly. In summer 2005, World Online decided to open-source the resulting software, which is, Django.
In order to make use of file-based sessions, you will need to set the SESSION_ENGINE setting to “django.contrib.sessions.backends.file”.
Django allows you to design your own URLs however you like. The aim is to maintain a clean URL scheme without any framework limitations.
In order to create URLs for your app, you will need to create a Python module informally called the URLconf or URL configuration which is pure Python code and is also a mapping between the URL path expressions to the Python methods.
The length of this mapping can be as long or short as required and can also reference other mappings.
When processing a request, the requested URL is matched with the URLs present in the urls.py file and the corresponding view is retrieved.
Django uses its own exceptions as well as those present in Python. Django core exceptions are present in django.core.exceptions class some of which are mentioned in the below:
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| AppRegistryNotReady | Raised when you try to use your models before the app loading process (initializes the ORM) is completed. |
| ObjectDoesNotExist | This is the base class for DoesNotExist exceptions |
| EmptyResultSet | This exception may be raised if a query won’t return any result |
| MultipleObjectsReturned | This is raised by a query if multiple objects are returned and only one object was expected |
| FieldDoesNotExist | This exception is raised by a model’s <_meta.get_field()> function in case the requested field does not exist |
Yes. Hardware is much cheaper when compared to the development time and this is why Django is designed to make full use of any amount of hardware that you can provide it.
Django makes use of a “shared-nothing” architecture meaning you can add hardware at any level i.e database servers, caching servers or Web/ application servers.
Django is not a CMS (content-management-system) . It is just a Web framework, a tool that allows you to build websites.
NoSQL basically stands for “not only SQL”. This is considered as an alternative to the traditional RDBMS or the relational Databases.
Officially, Django does not support NoSQL databases. However, there are third-party projects, such as Django non-rel, that allow NoSQL functionality in Django. Currently, you can use MongoDB and Google App Engine.
You can piggyback on top of an add/ change form that is automatically generated by Django, you can add JavaScript modules using the js parameter.
This parameter is basically a list of URLs that point to the JavaScript modules that are to be included in your project within a <script> tag. In case you want to do more rather than just playing around with from, you can exclusively write views for the admin.
A view in Django either returns an HttpResponse or raises an exception such as Http404. HttpResponse contains the objects that consist of the content that is to be rendered to the user.
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello_world(request):
html = "
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
"
return HttpResponse(html)
#### What should be done in case you get a message saying “Please enter the correct username and password” even after entering the right details to log in to the admin section? In case you have entered the right details and still not able to login to the admin site, cross verify if the user account has is_active and is_staff attributes set to True.
What should be done in case you are not able to log in even after entering the right details and you get no error message?
In this case, the login cookie is not being set rightly. This happens if the domain of the cookie sent out by Django does not match the domain in your browser. For this, you must change the SESSION_COOKIE_DOMAIN setting to match that of your browser.
How can you limit admin access so that the objects can only be edited by those users who have created them?
Django’s ModelAdmin class provides customization hooks using which, you can control the visibility and editability of objects in the admin. To do this, you can use the get_queryset() and has_change_permission().
Inconsistent row counts are a result of missing Foreign Key values or if the Foreign Key field is set to null=False. If the ForeignKey points to a record that does not exist and if that foreign is present in the list_display method, the record will not be shown the admin changelist.
The csrf_token is used for protection against Cross-Site Request Forgeries. This kind of attack takes place when a malicious website consists of a link, some JavaScript or a form whose aim is to perform some action on your website by using the login credentials of a genuine user.
No. Django only supports single-column Primary Keys.
First, make sure that your DEBUG setting is set to True. Then, type the following commands:
from django.db import connection
connection.queries
#### Is it mandatory to use the model/ database layer? No. The model/ database layer is actually decoupled from the rest of the framework.
You can make use of the RequestContext in case all your templates require the same objects, such as, in the case of menus. This method takes an HttpRequest as its first parameter and it automatically populates the context with a few variables, according to the engine’s context_processors configuration option.