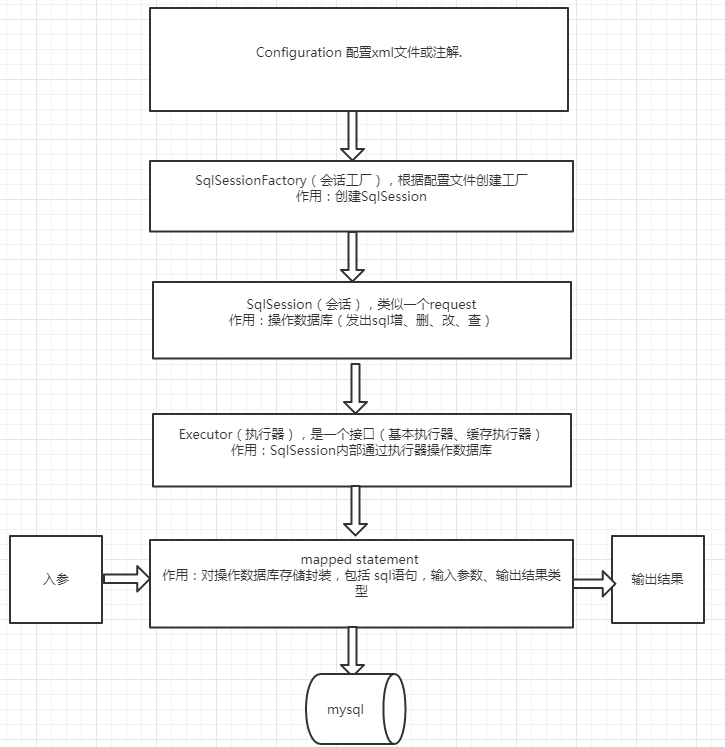
- mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>- *Mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.zwd.mybatis.proxy.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUserById"
resultType="com.zwd.mybatis.proxy.pojo.User" parameterType="int">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.zwd.mybatis.proxy.pojo.User">
insert into user (id,name) values (#{id},#{name})
</insert>
</mapper>- *Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
User selectUserById(int id);
void insertUser(User user);
}- 测试代码
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = null;
try {
user = userMapper.selectUserById(1);
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
System.out.println(user);
}mybatis使用代理的类在org.apache.ibatis.binding包下,有四个类为MapperMethod、MapperProxy、MapperProxyFactory、MapperRegistry. 顾名思义这里首先调用注册MapperRegistry,进入MapperRegistry断点打在addMapper中,走一遍调用链。
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);一直走下去会发现先把流放入到XMLConfigBuilder中,并调用parse
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());进入parse中发现如下代码
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));结合mybatis-config.xm文件可知,是对进行处理。继续下行
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}由此看出是对configuration下的所有属性进行读取,这里我们的配置文件中重点在mappers,其他可以不看。继续下行
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
//...
mapperParser.parse();
//...
}
//进入parse();
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
//...
}
//进入bindMapperForNamespace
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
//...
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
//...
}
//进入addMapper
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
// 进入addMapper
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
//...
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
//...
} 可见最终mapper对应的xml被放入mapperRegistry中。
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 进入getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
// 进入getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
// 进入getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
//...
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
//...
// 进入newInstance
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}可见代理对象是通过前期加载配置文件进行获取并使用jdk动态代理生成。
既然看到了这里,熟悉动态代理的都知道下一步应该是查看invoke方法的类了,没错invoke就写在MapperProxy中。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//...
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
//进入mapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
//...
}
case UPDATE: {
//...
}
case DELETE: {
//...
}
case SELECT:
//...
case FLUSH:
//...
default:到这里整个流程就走完结束。